* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Macromolecules 9-3
Ancestral sequence reconstruction wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
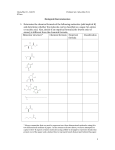
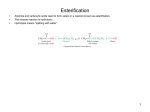
Macromolecules---Lipids and Proteins 9/3/2014 I. II. Yesterday we talked about dehydration synthesis and how removing one water molecule joins monomers together to form polymers a. This process can reverse b. The adding of a water molecule to a polymer, which breaks the polymer into a monomer is called hydrolysis Lipids a. DO NOT FORM POLYMERS b. “Water-Fearing” i. HYDROPHOBIC c. Three classes of biologically important lipids i. Fats ii. Phospholipids iii. Steroids d. Fats i. Composed of a glycerol 1. connects three fatty acids together 2. ii. And Three fatty acids 1. Very long chains of C, H, and O 2. Contain the most energy in the molecule iii. Fatty Acids vary in two ways 1. Number of Carbon Atoms 2. If they have any double bonds! iv. Saturated Fats 1. Contains maximum Hydrogen atoms 2. NO DOUBLE BONDS 3. BAD TO CONSUME 4. Come from Animal fats 5. Solid at room temperature v. Unsaturated Fats 1. At least one double 2. Plant/Fish sources 3. Liquid at room temperature 4. Considered best to consume 5. Two types of unsaturated fats a. Monounsaturated i. One double bond b. Polyunsaturated i. 2 or more bonds e. Phospholipids i. Remove one fatty acid chain from a regular fat ii. Replace the fatty acid with a PHOSPHATE (PO4) iii. Unique Property: 1. Fatty Acid “tails” are hydrophobic (Water-fearing) 2. Phosphate head is hydrophilic (water-loving) iv. In the presence of water, a phospholipid will self assemble into a bilayer v. The phospholipid forms the outer part that is contact with the water 1. The fatty acids form the inner part that is away from water 2. 3. This is the basic structure of all cellular membranes! III. Proteins a. 50% of the dry mass of a cell! i. Structure ii. Support iii. Storage iv. Transport v. Movement vi. Cellular communication b. Structure i. Made of chains of amino acids 1. 20 different amino acids combining in infinite ways 2. 2.43 x 10 ^ 18 combinations! (20x19x18x17…1) 3. Sequence of the amino acid determines the shape of the protein 4. The shape of the protein determines the function of the protein! c. Four Levels of Protein Structure i. Primary 1. Sequence of amino acids in the protein a. Determined by the structure of the DNA sequence in the nucleus! b. Every three letters in DNA codes for an amino acid c. These amino acids form chains to make proteins ii. Secondary 1. The folding and/or coiling of the protein chain 2. Caused by HYDROGEN bonds that occur between the amino acids 3. Two types of secondary structure a. Spiral shape (HELIX) b. Folded Sheet (PLEATED)