* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell - Capital High School
Survey
Document related concepts
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
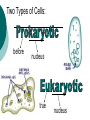
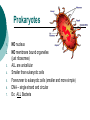
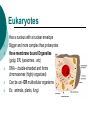
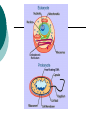
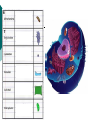
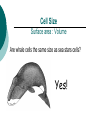
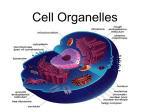
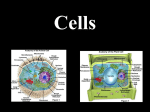
Cell Theory Prokaryote vs. Eukaryote Organelles, and Cell Size What is a Cell? Cell – Basic unit of living things. Organisms are either: Unicellular – made of one cell such as bacteria and amoebas. OR Multicellular – made of many cells such as plants and animals. Scientists to Remember Robert Hooke (1665) – Observed “cells” in cork Cell Theory Confirmed discoveries that all scientists believe to be true about cells: 1. Cells are the basic unit of life. 2. All living things are made of cells. 3. New cells are produced from existing cells. Two Types of Cells: before nucleus true nucleus Prokaryotes 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. NO nucleus NO membrane bound organelles (just ribosomes) ALL are unicellular Smaller than eukaryotic cells Forerunner to eukaryotic cells (smaller and more simple) DNA – single strand and circular Ex: ALL Bacteria Eukaryotes 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Has a nucleus with a nuclear envelope Bigger and more complex than prokaryotes Have membrane bound Organelles (golgi, ER, lysosomes…etc) DNA – double-stranded and forms chromosomes (highly organized) Can be uni- OR multicellular organisms Ex: animals, plants, fungi 1 2 Control Center: Holds DNA 2 Controls what goes in and out of cell; Protects Cell 3 Jelly Like Substance that holds organelles 4 5 Site of Protein Synthesis Protein and lipid synthesis; transport of proteins 5 1 3 4 6 7 6 7 Cell Membrane 1. Regulates what enters and leaves the cell. Selectively permeable Structure 2. Protects and supports the cell. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=LKN5sq5dtW4 Lipid bilayer http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=LKN5sq5dt W4 Cell Size Surface area : Volume Are whale cells the same size as sea stars cells? Yes! What limits the size of cells? Surface Area to Volume Ratio - How much space is on the outside (cell membrane) compared to the space on the inside of the cell. As the surface area of something increases, it’s volume increases faster Surface area = L x W x # of sides (cm2) the surface of an object. The outside covering of a cell. (cell membrane) Volume = L x W x H (cm3) The space inside the cell A small object has a high surface area to volume ratio A large object has a small surface area to volume ratio Large Cell It takes more time for the nutrients to reach the center of this cell & DNA would not be able to keep up with demands of the cell Small Cell It takes less time for the nutrients to reach the center of this cell Conclusion As cell size increases, the surface area to volume ratio Decreases (small surface area to volume ratio), which can lead to death of a cell. Having a large surface area to volume ratio is important to the functioning of cells since it gets materials, nutrients, O2, & wastes into & out of it faster. Cells divide before they get too big!