* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Biology 2121 – Lecture Sheet – ANS 1. The autonomic nervous sy
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry of Alzheimer's disease wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
End-plate potential wikipedia , lookup
Neural oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Multielectrode array wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Mirror neuron wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Basal ganglia wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Chemical synapse wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Pre-Bötzinger complex wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
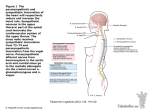
Biology 2121 – Lecture Sheet – ANS 1. The autonomic nervous system contains ______________ neurons only. They service organs with ____________ or __________ muscle tissue. 2. The two divisions of the ANS are the __________________ and ____________________ divisions. 3. The term duel innervation means: _______________________________________________________ 4. The parasympathetic division is referred to as the ___________________________________. 5. The sympathetic division is referred to as the ____________________________________. 6. Provide a couple of examples of what the sympathetic nervous system does to organs. 7. Do the same for the parasympathetic system below: 8. What is vasomotor tone? Which ANS division controls this? 9. The ___________________ division of the ANS causes an erection to occur during sexual activity, and the ______________ division is responsible for an ejaculation. 10. The parasympathetic division promotes increased __________________ during digestion. The sympathetic system would __________________ the anal sphincters and decrease the ____________ and smooth muscle of the digestive system. 11. Determine the effects of the parasympathetic and sympathetic system on each of the following organs. Organ Iris of the Eye Parasympathetic Sympathetic Salivary glands Sweat glands Heart muscle The Heart Lungs 12. Explain the role of the sympathetic nervous system on thermal regulation of the body. 13. All somatic motor neurons release the neurotransmitter _________________. The ANS neurons release ______________ and ____________________. 14. Somatic motor neurons are ______________ myelinated and the ANS are __________________________ mylenated. 15. The ANS is a one-neuron unit and the ANS motor neurons are composed of _______ neurons called the ____________________ neurons and ____________________ neurons. 16. All sympathetic preganglionic axons release the neuron transmitter _________. The postganglionic axons release _________________ or ____________________. 17. All preganglionic cell bodies of the ANS reside in the _____________ ________ or brain. 18. All sympathetic neuron cell bodies of postganglionic neurons lie in the ________________ ___________ ganglia. Postganglionic cell bodies of parasympathetic neurons lie very close to the ________________. 19. Fibers that release the neurotransmitter ACh are called ________________ fibers. All fibers that release norepinephrine are called ____________ fibers. 20. When ACh binds to nicotinic receptor the response is always ______________. 21. Complete the neurotransmitter receptor table below: Neurotransmitter Acetylcholine Receptor Location Effects of Binding Nicotinic Muscarinic Norepinephrine Beta 1 Beta 2 Beta 3 Alpha 1 Alpha 2 22. The four parasympathetic nerves which originate in the cranial area are the _________________, __________________, ________________________, _________________________. 23. The function of CN III (oculomotor) is to cause the pupil to ______________ and the lens to ______________. 24. The function of CN VII is to stimulate secretions of the _____________ and _____________ glands. 25. CN IX activates the _____________ salivary gland . 26. CN X innervates the ___________, _____________ and most _____________ organs down to the proximal large intestine. 27. Parasympathetic outflow from the sacral area innervates the distal ___________________, urinary ___________ and the ____________ and the reproductive organs. 28. The nerves that leave the sacral area via the ventral rami are called the __________________ nerves and join to form the __________________ plexus. 29. The cell bodies of the sympathetic preganglionic neurons can be found in this portion of the spinal cord: _____________. They exit via the _______________ horns of gray. 30. All preganglionic neurons that synapse in the chain ganglia move from the ventral rami through the White Ramus ___________ to the ganglia. After synapsing in the chain ganglia they exit and move towards their target organs through the __________ ramus ___________. 31. Not all synapse in the chain ganglia. Some preganglionic neurons by pass the ganglia and synapse in the ___________ ganglia (example the celiac ganglia). These form the sympathetic ________________ nerves. 32. The lumbar splanchnic nerves innervate the _____________________________. The greater splanchnic nerves innervate the _______________________. The lesser splanchnic nerves innervate the _______________________________. 33. Sympathetic nerves originating in T1-T4 innervate the __________ region including the organs ________________________________. 34. T1-T6 innervate the ____________________region. They innervate the heart via the _____________ plexus. 35. T5-L2 bypass the chain ganglia and synapse in the ________________ ganglia. They form the _______________ nerves. 36. T5-L2 nerves serve the _____________________________________________________. 37. T10-L2 nerves serve the ____________________________________________________.