* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 2-immune system
Survey
Document related concepts
Gluten immunochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Sociality and disease transmission wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Herd immunity wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Social immunity wikipedia , lookup
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
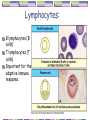
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Immunosuppressive drug wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
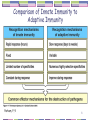
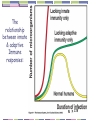
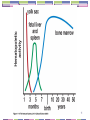
Overview of The Immune System: 1 Outline for Lectures 2 & 3 The immune system is designed to eliminate pathogens. Who are the infectious agents? Overview of the two arms of the immune system: innate immunity & adaptive immunity. What are the cell types involved with immune responses? What are the important immunological tissues? 2 Parham, p. 3 How do pathogens enter into the human body? What barriers are present in the human body to prevent entry/infection by pathogens? 3 Would the immune response towards each type of pathogen be identical? Parham, p. 4 4 Innate Immunity Adaptive Immunity (acquired) Humoral immunity & Cell Mediated Immunity 5 Comparison of Innate Immunity to Adaptive Immunity Parham, P. 9 6 The relationship between innate & adaptive Immune responses: p. 228 7 The innate immune response is essential for elimination of a pathogen but not sufficient. The adaptive immune response requires certain key players of the innate immune response to become activated. 8 The components of the immune system Overview of Cell Types important in immunology 9 Where do the cells of the immune system come from? Leukocytes Hematopoiesis: Hematopoietic stem cells from the bone marrow Undifferentiated Pluripotent Self-renewing 10 11 Progenitors: -Not selfrenewing -Committed to differentiation Granulocyte/ macrophage progenitor 12 What stimulates the differentiation of stem cells & progenitor cells? Hematopoietic Inducing Microenvironment: Requires bone marrow stromal cells & growth factors (cytokines). Kuby, Immunology, fig. 2-2 13 The leukocytes (WBC) Kuby Immunology 14 The Cells Important in Immunology A Closer Look 15 Lymphocytes: B lymphocytes (B cells) T lymphocytes (T cells) Important for the adaptive immune response. 16 B cells: Surface receptor = Immunoglobulin (Ig). Humoral Immunity. kuby 17 T cells: Helper T cells (Th cells): T cell Receptor (TCR) CD4+ Produce cytokines & direct immune responses. Cytotoxic T cells (Tc or CTL): TCR+ CD8+ Cytotoxic 18