* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nervous filled
Neuroscience and intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Dual consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Lateralization of brain function wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Functional magnetic resonance imaging wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Neurogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Causes of transsexuality wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Human multitasking wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry of Alzheimer's disease wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Mind uploading wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Neurotechnology wikipedia , lookup
Sports-related traumatic brain injury wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neuroprosthetics wikipedia , lookup
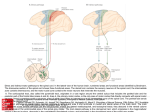
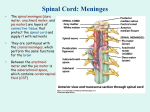
Nervous System A major control and communication system Brain Myths #1: You only use 10 percent of your brain. #2: Doing crossword puzzles can keep your brain young. #3: A person's personality displays a right-brain or leftbrain dominance. #4: Brain damage is always permanent. #5: Drinking alcohol kills brain cells. Neuron • “neur-” means nerve, so a neuron is a nerve cell • Cell body is the part where the organelles, such as the nucleus, are located • Dendrite is the receiving end of the neuron • Axon is the transmitting or conducting end of the neuron Nerve • A group of neurons (specifically their axons) that are bundled together anywhere except the brain/spinal cord, is termed a nerve Nerve impulse • A nerve impulse is an electrical message traveling along a neuron. Synapse • A junction between adjacent neurons • Neurotransmitters are chemicals carrying nerve message across the synapse Myelin • Some neurons have their axons coated in a fatty substance called myelin. • Myelin increases the speed of nerve impulse transmission – as high as 200 mph • White matter Central Nervous System • Brain • Spinal Cord • Control, information processing • Thoughts are formed • Memory is stored Peripheral Nervous System • Carries messages to and from the CNS • Sensory – carries information towards the CNS • Motor – carries information away from the CNS to the muscles and glands PNS • Somatic motor information travels to skeletal muscles • Autonomic motor information travels to cardiac muscle, smooth muscle and glands; responsible for your Fight or Flight response Brain • “enceph-” means brain • Located in skull • Medulla oblongata is part of the brainstem and controls important reflexes that control breathing, heart rate and blood pressure. Also is the site where motor and sensory pathways cross. Brain • Hypothalamus is a center of homeostasis mechanisms such as hunger, thirst, water balance, temperature regulation; makes hormones, and controls the Autonomic Nervous System. Brain • Thalamus is a sensory relay center Brain • Cerebrum is the largest and highest center of the brain • Responsible for conscious awareness, thinking, intelligence, memory and deciding your response to sensory input. Brain • Electroencephalogram, or EEG, is a recording of the brain’s electrical activity, commonly called brain waves. Spinal cord • “myel-” means spinal cord • Located within your vertebrae • Sends sensory messages to your brain • Carries motor messages away from your brain Spinal Reflexes • A reflex is an autonomic, quick response to a stimulus. The reflex is repeatable. • Spinal reflexes involve the spinal cord and do not involve conscious thought from the brain. Spinal reflex CNS Meninges • Meninges are tough, protective membranes that surround the brain and spinal cord. • Within the meninges is Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) that cushions and provides nourishment for the CNS • What is meningitis? Nervous System Pathology • Brain damage • The brain requires oxygen for aerobic metabolism. Lack of oxygen for more than 5 minutes can kill brain cells. • The brain requires glucose for metabolism. Lack of glucose for more than 15 minutes kills brain cells. • Neurons cannot undergo mitosis. Epilepsy • Brain fires abnormal signals that travel to skeletal muscles. • Skeletal muscles contract leading to seizures. • May lose consciousness in larger seizures • Causes are injury, infection, genetic predisposition, and many causes are unknown Epilepsy • Treatments include correcting the cause, if known; drugs and/or surgery • Decreasing the frequency and magnitude of the seizures with medications. Multiple Sclerosis • Many “hard” scars form along the myelin sheaths of neurons • Autoimmune disease • Numerous short circuits occur resulting in difficulty in vision, memory, walking and judgment • Chronic disease that progresses slowly Cerebral Palsy • Motor centers are damaged at the time of birth • Causes include German Measles, radiation exposure, oxygen starvation to the baby’s brain at the time of delivery • Results in varying degrees of impairment of motor abilities.