* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download active transport
Survey
Document related concepts
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
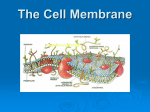
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
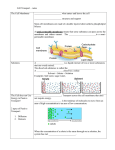
active transport the movement of chemical substances, usually across the cell membrane, against a concentration gradient; requires cells to use energy carrier protein a protein that transports substances across a cell membrane concentration gradient a difference in the concentration of a substance across a distance contractile vacuole in protozoans, an organelle that accumulates water and then releases it periodically to maintain osmotic pressure cytolysis the bursting of a cell diffusion the movement of particles from regions of higher density to regions of lower density endocytosis the process by which a cell membrane surrounds a particle and encloses the particle in a vesicle to bring the particle into the cell equilibrium in biology, a state that exists when the concentration of a substance is the same throughout a space exocytosis the process by which a substance is released from the cell through a vesicle that transports the substance to the cell surface and then fuses with the membrane to let the substance out facilitated diffusion the transport of substances through a cell membrane along a concentration gradient with the aid of carrier proteins hypertonic describes a solution whose solute concentration is higher than the solute concentration inside a cell hypotonic describes a solution whose solute concentration is lower than the solute concentration inside a cell ion channel a pore in a cell membrane through which ions can pass isotonic describes a solution whose solute concentration is equal to the solute concentration inside a cell osmosis the diffusion of water or another solvent from a more dilute solution (of a solute) to a more concentrated solution (of the solute) through a membrane that is permeable to the solvent passive transport the movement of substances across a cell membrane without the use of energy by the cell phagocyte a cell that ingests and destroys (digests) foreign matter or microorganisms phagocytosis the process by which a cell engulfs large particles or whole cells, either as a defense mechanism or as a means to obtain food pinocytosis a method of active transport across the cell membrane in which the cell takes in extra cellular fluids plasmolysis the contraction or shrinking of the cell membrane of a plant cell in a hypertonic solution in response to the loss of water by osmosis sodium-potassium pump a carrier protein that uses ATP to actively transport sodium ions out of a cell and potassium ions into the cell turgor pressure the pressure that is exerted on the inside of cell walls and that is caused by the movement of water into the cell vesicle a small cavity or sac that contains materials in a eukaryotic cell; forms when part of the cell membrane surrounds the materials to be taken into the cell or transported within the cell