* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File - Sheffield Peer Teaching Society
Survey
Document related concepts
Herd immunity wikipedia , lookup
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Autoimmunity wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Sjögren syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
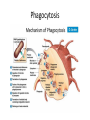
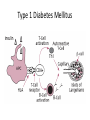
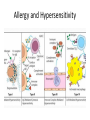
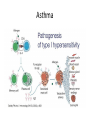
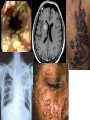
Phase 2a Revision Session Faiza Shafiq and Natasha Ngonyamo 06/03/17 The Peer Teaching Society is not liable for false or misleading information… Learning objectives • Innate immunity • Adaptive immunity • Autoimmune diseases – Type 1 diabetes mellitus – Hashimoto’s thyroiditis • Hypersensitivity and allergy – Asthma • Immunodeficiency – HIV Definitions • Immunity • Ability to ward off disease/ disease causing organism • Innate Immunity • Present at birth • Non-selective • No memory • Adaptive immunity • Built up over time • Specific • Memory response (to previous disease/ vaccination) Innate vs Adaptive Immunity • Innate – – – – Barriers Inflammation Interferon Macrophage/ opsonisation – Phagocytosis/ MAC • Adaptive – – – – – Lymphocyte B cells, T cells MHC Lymphoid organs Mast cells The Peer Teaching Society is not liable for false or misleading information… Innate Immunity Cellular component • • • • • Neutrophils Macrophages Lymphocytes Basophils Eosinophils Chemotaxis The Peer Teaching Society is not liable for false or misleading information… Adherence Phagocytosis Adaptive immunity • Antigen presenting cells • Mainly macrophages • Dendritic cells • Some B cells • Major histocompatibility complex (MHC) • Proteins that mark a cell as self • Class 1- all cells • Class 2- Certain immune cells • T helper cells • Stimulate proliferation of other T cells • Stimulate B cells • Cytotoxic T cells • Destroy infected body cells (apoptosis) • B cells • Produce antibodies Immunology in Disease Autoimmune diseases • Definition – A disease in which the body produces antibodies that attack its own tissues, leading to a pathological process • What autoimmune conditions do you know of? Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Clinical Features • • • • • • • • Polyuria Polydipsia Weight loss Lethargy Fatigue Recurrent infections Juvenile onset DKA Diagnosis • Fasting glucose >/=7.0mmol/L • OGTT >/= 11.1mmol/L • HbA1c 48mmol/mol Management • Lifestyle factors • Insulin!!!! – What do we need to watch out for? Hashimoto’s Thyroditis • Destruction of thyroid cells by various cell and antibody-mediated immune processes • Antibodies blocking the TSH receptors have been described Clinical features Diagnosis and Management • Diagnosis – TFTs – Autoantibodies • Anti- thyroid peroxidase (anti-TPO) – 90% of patients • Anti-thyroglobulin antibodies – Less specific – Also found in Grave’s disease • Management – Levothyroxine Allergy and Hypersensitivity Asthma Clinical presentation • Signs – Polyphonic wheeze – Hyperinflated chest – Increased RR – Low oxygen Sats – Long expiratory phase – Use of accessory muscles • Symptoms – SOB – Cough – Diurnal variation – Triggers – History of atopy – Chest tightness Diagnosis • Spirometry – FEV1/FVC <0.7 • Reversibility of symptoms with bronchodilator Management Immunodeficiency • Primary immunodeficiency syndromes – Antibody deficiency • Selective IgA deficiency – Cell mediated immunity deficiency • Thymic aplasia (DiGeorge syndrome) • Severe combined immunodeficiency disease (SCID) • Secondary immunodeficiency syndromes – Malnutrition – HIV – Drugs- cytotoxic, immunosuppressants Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) • HIV virus specifically targets cells expressing CD4 – Mainly CD4 T cells – Causes CD4 T cell depletion • Direct cytotoxicity • Immune system over-activation • Sexual transmission Clinical Features Acute Primary HIV Infection • • • • • • • • • FEVER 38°C - 40°C Sore throat Sweats ++ Diarrhoea Headache Myalgia + arthralgia Mild hepatosplenomegaly & lymphadenopathy Rash Mouth ulcers Clinically Latent Phase • Persistent generalised lymphadenopathy Early Symptomatic HIV • • • • • • Oral candidiasis Oral hairy leukoplakia VZV CIN Peripheral neuropathy Constitutional symptoms AIDS • CD4 count <200 • Resp – Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia – Bacterial pneumonia – strep pneumoniae – TB • CNS – Cerebral toxoplasmosis – Tuberculoma – Meningitis • Neoplasms – – – – Kaposi’s sarcoma Cervical neoplasia Lymphoma Molluscum contagiosum Management • Highly active anti-retroviral therapy • Aim to reduce viral load to <50 copies/ml and increase CD4 count