* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Affective Computing
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognition wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Prenatal memory wikipedia , lookup
Situated cognition wikipedia , lookup
Perception of infrasound wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Conditioned place preference wikipedia , lookup
Executive functions wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive psychology wikipedia , lookup
Background music wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Multisensory integration wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive development wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Traumatic memories wikipedia , lookup
Meta-emotion wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy of memory wikipedia , lookup
Emotion in animals wikipedia , lookup
Risk aversion (psychology) wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Psychophysics wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus modality wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Affective neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Emotion perception wikipedia , lookup
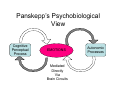
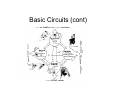
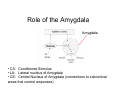
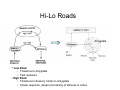
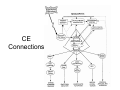
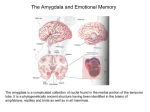
Affective Computing “Bottom-Up” Views Lecture 3 Appraisal Theory Appraisal Theory: Stimulus ➞ Cognitive Appraisal ➞ Emotion But is emotion always post-cognitive (require cognition) Zajonc: Rejects that Affect is Post-Cognitive • Zajonc, 1980 – Rejects Cognitive Appraisal View that presumes (cognitive) appraisal precedes affective reactions Zajonc View: The Basis • • • • • • Affective Reactions are primary Affect is basic (universal) Affective reactions are inescapable Affective judgments tend to be irrevocable Affective judgments implicate the self Affective judgments are difficult to verbalize – Cf non-verbal • Affective reactions need not depend on cognition • Affective reactions may become separated from content Zajonc View: Evidence • Affective Reactions show phylogenetic and ontogenetic primacy • Separate neuroanatomical structures can be identified for affect and cognition (1984) • Appraisal and Affect are often uncorrelated and disjoint • New affective reactions can be established without apparent participation of appraisal – Taste aversion – Repeated exposure preferences w/o recognition • Affective states can be induced by non-cognitive and non-perceptual procedures – Drugs, hormones – Facial action such as smiling (Ekman et al) Preference vs Familiarity – We like things we have seen or heard before • Novelty also key component of appraisal • Does it hinge on subjective recognition – Experiments: • Dichotic listening experiment (Wilson) • Rapid (1ms) random polygon presentation – Results: • Liking w/o subjective recognition • Liking is better than “conscious” recognition at distinguishing old and new stimuli • Subjects far more confident of their liking judgments • Affective judgments faster • Novelty/familiarity not mediating affect – Your first guess is your best guess Comments • Zajonc blurs cognition & consciousness – Cognitive Appraisal: Subsuming of cognition by emotion • Key question remains: – how do cognition and emotion interrelate • Point to remember – Does appraisal require cognition or inference at all Affective Neuroscience Basic Circuits / Emotion Categories • Jaak Panskepp • Basic, distinct emotion circuits in the brain – Distinct emotional patterns can be evoked by stimulating electrically particular subcortical areas responsible for basic emotions • Cortical regions largely free of such effects • “Essence of emotionality is subcortical and precognitively organized” – Nevertheless cortical appraisal and memory processes modify and are modified by emotions – No emotional state is free of cognitive influence Emotion rooted in ancient recesses of mammalian brain Evolution adds layers that mediate stimulus and response by more sophisticated sensory processing, learning & memory Evolution Note : Lisencephalic mammals have smooth cortexes while primates have folded cortexes with more surface area (allows more neurons) Alternative views on role of affective consciousness in emotional adaptation 1. Stimulus ➞ Interpretation ➞ Feeling ➞ Bodily Response 2. Stimulus ➞ Interpretation ➞ Bodily Response ➞ Feeling 3. Stimulus ➞ Interpretation ➞ Bodily Response ➞ Feeling ➞ Attribution 4. Panskepp’s Psychobiological View Cognitive Perceptual Process EMOTIONS Mediated Directly Via Brain Circuits Autonomic Processes Role: Regulation of response • Affective experiences are generated by neuronal mechanisms • Mechanisms arose to respond to lifeimpacting events over course of evolution • Beyond reflexive response – It is more adaptive to anticipate future needs than simply respond to immediate – Must adapt both thru evolution and learning Basic Circuits • • • • • • • • Fear Anger Sorrow Anticipatory eagerness Play Lust Maternal nurturance Others? – Ongoing research Basic Circuits (cont) Implications • Basic Circuits – Emotion Categories arise from these circuits – Guide Responses • Evolutionary roots • Potential Impact on learning – Associative learning probably linked to emotion circuits • Ontogenetic effects Example: LeDoux QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. Fear Conditioning in the Rat Fear Conditioning • Initially neutral stimulus (conditioned stimulus) can acquire affective properties if paired with a biologically significant event (unconditioned stimulus) • Pair audio tone (conditioned stimulus) with electric shock (unconditioned stimulus) • Rat eventually learns to react aversively just to tone • Then study learned pathways and role of various brain regions via • Staining of neurons and dissection • Impact of lesions on behavior Key to Regions Studied • Amygdala – Forms association of tone with reaction – Part of the cortex (cognitive processing, more recently evolved area) – Connects cortical to subcortical (older, reflexive behavior) – Has 12 (or more) subcomponents or nuclei • Thalamus – Processing of stimuli • Sensory/Auditory Cortex – More sophisticated processing/analysis of stimuli Role of the Amygdala Role of the Amygdala Amygdala • CS: Conditioned Stimulus • LA: Lateral nucleus of Amygdala • CE: Central Nucleus of Amygdala (connections to subcortical areas that control responses) Hi-Lo Roads Amygdala • Low Road: • Thalamus to Amygdala • Fast response • High Road: • Thalamus to Sensory Cortex to Amygdala • Slower response, deeper processing of stimulus in cortex Contextual Fear Conditioning • Hippocampus also plays role • Forms memory representations of different situations. • Provides amygdala with contextual information • Allows response to be conditioned to given stimulus in given situation. • Thus emotional reaction will be appropriate for that context • Example: Rat’s fear response elicited when returned to chamber where shock was delivered CE Connections Studies of Human Amygdala • Brain Damage – to Amygdala • impacts perception of emotional expressions & voices • Impacts Fear Conditioning – to Hippocampus • Impacts fear conditioning to context • Functional Imaging – Fearful/angry faces activate amygdala more than happy ones – Fear conditioning leads to increased amygdala activity Human Amygdala Pathways to and from cortical regions Amygdala once activated by sensory events from thalamus or cortex: • Regulates cortical areas that project to it • Influences cortical sensory processing thru arousal networks that innervate cortical areas and bodily feedback that impacts cortical area • Interacts with medial prefrontal cortex and dorsolateral prefontal cortex that: – Influence cognitive function – Regulate amygdala LeDoux: Feeling/Conscious Emotion ? Caveat: Rat Studies Points • Emotions involve primitive circuits – Preserved across evolution – Basic Categories • Coupling between emotion and cognition circuits is complex • Components complex – Amygdala has 12 centers (nuclei) • Emotion memories versus non-emotional memories – Emotional memories persistent – Non-emotional can extinguish emotional Points (cont) • Parallel routes of processing of emotional stimuli – Thalamic-amygdala (Fast) – Cortical-amygdala (likely regulates fast route) • Separate inputs to emotional eval – Fear: • Simple stimuli (LA-CE) • Complex stimuli (hippocampus-B/AB-CE) • Emotion expression are triggered centrally • But specific expressions determined locally – Lateral hypothalamus - blood pressure – Gray - freezing