* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CELL PART DESCRIPTION/LOCATION FUNCTION 1. Cell
Survey
Document related concepts
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
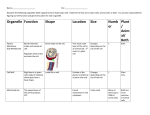
CELL PART DESCRIPTION/LOCATION FUNCTION 1. Cell Membrane External boundary of the cell. 1) Serves as external cell barrier; 2) Regulates entry and exit of materials 2. Lysosomes Sacs in cytoplasm Contains enzymes to digest cell wastes (are the “clean-up crew”) 3. Mitochondria Rod-like structures in cytoplasm Site of ATP synthesis! Is powerhouse of cell 4. Microvilli Projections of plasma membrane Increase surface area of the cell 5. Golgi Apparatus A stack of smooth membrane sacs close to nucleus 6. Centrioles Two rod-shaped bodies near the nucleus Packages & modifies proteins to send to other organelles and outside the cell Forms the spindle for mitosis (cell division) 7. Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER) Sacs and tubules in cytoplasm (without ribosomes) Produces lipids & steroids and performs drug detoxification 8. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER) Sacs and tubules in cytoplasm; have ribosomes attached to them Proteins are modified and sent to Golgi apparatus. Also synthesizes phospholipids and cholesterol 9. Ribosomes Tiny particles composed of RNA and protein attached to RER and also scattered in cytoplasm Synthesizes (makes) proteins 10. Cilia Short cell surface projections; looks like tiny hairs Move in unison, so propels materials across cell surface in one direction 11. Microtubules Cylindrical structures extending across cell interior Support cell and give it shape (cytoskeleton). Involved in cell movement 12. Perioxisomes Sacs of enzymes, especially catalase Mainly breaks down hydrogen peroxide. 13. Microfilaments Tiny rods running through cell interior Helps in muscle contraction, moves the cell or cell parts Transcription In the nucleus Process that makes RNA from DNA Translation In the cytoplasm, at the ribosome Process that makes protein from RNA Replication In the nucleus The process of copying DNA during the S phase of the cell cycle Triplet In the nucleus The 3 nucleotide base of DNA Codon In the nucleus/cytoplasm The 3 nucleotide base of mRNA Anticodon Nuclear Structure Nucleus In the cytoplasm General Location & Appearance Located in cytoplasm; is usually round or ovalshaped; surrounded by nuclear membrane The 3 nucleotide base of tRNA. Function Control center for cell; DNA here contains the code to determine what proteins will be made. This determines what the cell will look like and do. Nucleolus Inside nucleus, usually round. Made of rRNA and proteins. Makes ribosomes. Chromatin Is located in the nucleus and is made of DNA and proteins. Directs cell’s activities by 1) Passing on information when the cell divides, & 2) directing production of proteins (see “nucleus” section). Nuclear membrane (envelope) Double membrane structure with pores. Surrounds nucleus. Wraps around nucleus, containing the nucleoplasm; regulates passage of materials to and from cytoplasm.