* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Practice Exam 3
Epigenetics in stem-cell differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Mir-92 microRNA precursor family wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
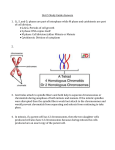
Bio 211 3.28.7 Practice Exam IIIa 1.) Through a microscope, you can see a cell wall beginning to develop arcoss the middle of the cell and the nuclei re-forming an either side of the cell wall. The cell is most likely: a. an animal cell in the process of cytokinesis b. a plant cell in the process of cytokinesis c. a bacterial cell dividing d. an animal cell in the S phase of the cell cycle 5.) A human cell containing 22 autosomes and a Y chromosome is: a. a somatic cell of a male b. a zygote c. a somatic cell of a female d. a sperm 6.) Homologous chromosomes move toward opposite poles of a dividing cell during: a. mitosis b. meiosis I c. meiosis II d. fertilization e. binary fission 7.) Crossing over usually contributes to genetic variation by exchanging chromosomal segments between: a. sister chromatids of a chromosome b. chromatids of nonhomologous chromosomes c. nonsister chromatids of homologues d nonhomologous loci of the genome 8.) Meiosis II is similar to mitosis in that: a. homologous chromosomes synaps b. DNA replicates before the division c. the daughter cells are diploid d. sister chromatids separate during anaphase 9.) A heterozygous individual is crossed with a homozygous dominant individual. The probablility of getting a heterozygote is: a. 0 b. .25 c. .50 d. .75 11.) In mice, grey coat color is( mix of black and white hairs) occurs in the heterozygous individuals (Gg). When two grey mice are crossed, the phenotypes of the progeny are 1black:2grey:1white. Which of the following of the crosses would produce the highest percentage of grey mice? a. Grey X Grey b. Grey X Black c. White X Black d. White X Grey 12.) There is good evidence for linkage when: a. multiple alleles are found b. a gene is recessive to a dominant allele c. two genes work together to control a specific characteristic d. genes do not segregate independently during meiosis e. blending inheritance occurs 13.) A recessive allele in the X chromosome is responsible for hemophilia in humans. A woman with normal blood clotting whose mother was a hemophiliac marries a man who has normal blood clotting. Which of the following is possible: a. They may have daughters with hemophilia b. They may have hemophilic sons c. none of their children could have hemophilia e. all of the above d. none of the above 14.) The ABO blood types in humans is an example of: a. multiple alleles b. epistasis c.pleiotrophy d. polygenic inheritance 15.) ___________ occurs when a gene at one locus alters the expression of a gene at a second locus. ____________ is an additive effect of two or more genes on a single phenotypic character. a. pleiotrophy; epistasis b. epistasis; polygenic inheritance c. polygenic inheritance: epistasis d. epistasis; pleiotrophy 17.) Crossing over is important because: a. it causes segregation b. it aligns the chromosomes at metaphase II of meiosis c. it creates new combinations of alleles on homologous chromosomes d. it causes mutations 18.) Which of the following is not an observation or inference on which natural selection is based? a. There is heritable variation among individuals. b. Poorly adapted individuals never produce offspring. c. There is a struggle for limited resources, and only a fraction of offspring will survive d. Individuals whose characteristics are best suited to the environment generally leave more offspring than those whose characteristics are less well studied. e. Organisms interact with their environment. 20.) A geneticist mixed together many different kinds of fruit flies- some with long wings, some with short wings, some with red eyes, and some with brown eyes. He allowed the flies to feed, mate randomly, and reproduce by the thousands. After many generations, most of the flies in the population had medium length wings and red eyes, and most of the extreme types disappeared. This illustrates: a. stabilizing selection b. diversifying selection c. fitness d. genetic drift 21.) In a population that is in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium, the frequency of a recessive allele in the gene pool is 0.7. The frequency of organisms in this population with the homozygous dominant genotype will be: a. 49% b.14% c. 21% d. %9 e. 7% 23.) A bottleneck event is a non-adaptive feature that: a. shows a fluctuation in allele frequencies b. results in a large population crash c. results in crossing over d. all of the above e. none of the above 24.) The largest unit within which gene flow can readily occur is a a. population b. species c. genus d. hybrid e. phylum