* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Crossing Over and Independent Assortment Notes
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
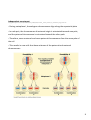
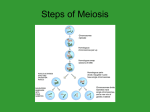
Topic 5 ‐ Crossing over and independent assortment Why aren’t offspring identical to each other if they all get half chromosomes from dad and half from mom? http://highered.mcgraw‐hill.com/sites/dl/free/0072835125/126997/animation5.html (on next page) In meiosis, the new cells have different combinations of genetic material than the parent cell n As opposed to mitosis in which the daughter and parent cell have identical genetic material Meiosis produces genetically different cells through two different processes n Independent assortment n Crossing over Crossing over When homologous chromosomes pair up during prophase I (synapsis), they may exchange pieces of chromosome This is known as crossing over As a result, individual chromosomes contain some genes of maternal origin and some genes of paternal origin. Gene – a specific unit of DNA that expresses a certain trait Allele – different forms of the same gene ‐ Expressed on homologous chromosomes 1 2 Independent assortment http://highered.mcgraw‐hill.com/sites/0072495855/student_view0/chapter3/animation__random_orientation_of_chromosomes_during_meiosis.html During metaphase I, homologous chromosomes align along the equatorial plate In each pair, the chromosome of maternal origin is orientated towards one pole, and the paternal chromosome is orientated toward the other pole. Therefore, some maternal and some paternal chromosomes face the same pole of the cell This results in new cells that have mixtures of the paternal and maternal chromosomes 3