* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Temporal Aspects of Visual Extinction
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Cortical cooling wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Executive functions wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Sensory substitution wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Eyeblink conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Affective neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Emotional lateralization wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Anatomy of the cerebellum wikipedia , lookup
Evoked potential wikipedia , lookup
Cerebral cortex wikipedia , lookup
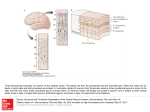
Neurology 1 CNS Gross Anatomy Donna Quezada, DC, DICCP, DIBCN With some slides by Chris Rorden [email protected] Roles of the CNS • Functions of neurons in the CNS (brain and spinal cord) include: – Sensor: Receives environmental and body stimuli – Integrator: Combines information received – Effector: Initiates body movements – Regulator: Maintains homeostatic state for body function 2 Nervous System • The CNS is protected and isolated. – Bone offers protection from injury • Skull covers brain • Vertebral Column covers spinal cord – The is encased in soft-tissue membranes – The brain’s blood vessels stop many subastances from entering the brain (blood-brain barrier) • Protects from contamination/infection – The brain floats in cerebral spinal fluid • Offers protection from impact 3 The Meninges • Dura Mater: Tough outer covering • Arachnoid Mater: Middle layer • Pia Mater: Inner closely formed layer 4 Brain Membranes: Meninges • 3 layers – Drua Mater (Tough Mother) aka: pachymeninx • Tough outer layer, connects brain to bone – Arachnoid Mater (Spidery Mother) • Spidery middle layer, connects Dura to Pia • Allows room for the cerebral spinal fluid • Allows movement of the CNS within its boney housing – Pia Mater (Small Mother) • Thinner, glossy layer next to the brain Dura – Functions • Houses blood vessels and sinuses • Main blood supply: middle meningeal artery • Forms septa to encapsulate the brain – Falx Cerebri • Syuperior and inferior sagittal sinuses – Tentorium Cerebelli • Straight sinus (at junction of F. Cerebri and Tentorium) • Transverse sinus • Sigmoidsinus – Diaphragma Sellae (covers the sella turcica) – Falx Cerebelli Arachnoid • Delicate, transparent • Attached to the dura • Separate from the pia by the subarachnoid space – Contains trabeculae: crossing fibrous bands – Cisterns: enlarged subarachnoid spaces • Arachnoid villi – Project into superior sagittal and other sinuses – Permit CSF flow into the venous system Pia • Highly vascular • Loose connective tissue • Invests the small blood vessels to the brain and spinal cord • Contributes to the – roof of the 3rd ventricle – Choroid plexuses of the 3rd and 4th ventricles • With arachnoid = leptomeninges (slender) Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) • Located between the meninges and in the ventricular cavities of the brain • Produced in the ventricular cavities by the choroid plexus • Functions – mechanical buffer – fluid for metabolic functions 9 "Copyright © 2005 by Thompson Delmar Learning, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED" CSF • CSF is in ventricles, subarchnoid space, interventricular foramens, and around the spine. • Circulates from ventricles around brain and spinal column • Is finally absorbed by venous system • Replenishes at ventricles every 7 hours 10 Ventricles • Lateral Ventricles • Connected by interventricular foramen • Collateral trigone area • Posterior and inferior horns • Connects to Third Ventricle through Monro’s foramen 11 Ventricles • Birds Eye View – Usually symmetrical in healthy people 12 Other ventricles… • Third Ventricle • Ventral to the corpora quadrigemina • Surrounded by central gray area • Connects to fourth ventricle through Cerebral Aqueduct • Fourth ventricle – Near Pons / Medulla 13 Ventricles 14 Ventricles in clinical setting • Hydrocephalus – E.G. cyst 15 Major Structures of the Brain 16 Brain Superior View Brain Inferior View Brain Lateral View Midsagittal Brain Cerebral Cortex • Convuluted to increase surface • Infintile reflexes and reactions come and go as this develops • 14-16 billion neurons reside in the gray matter • • • • Gyri (bumps) Sulci (grooves) Fissures (deep sulci) More neurons = more gyri • Lobes named for covering bones Function of Cortical Areas • Precentral Gyrus: motor control • Postcentral Gyrus: Somatosensory cortex • Sensory humunculus is more region specific than the motor (fuzzy) • Occipital lobe: vision, motor and sensory association • Temporal: Hippocampal and paracampal areas – Speech – Auditory Association – Memory • Speech: two parts – Motor: Inferior frontal lobe: Brocca’s – Expressive: Wernicke’s Aphasia (BA 44) temporal lobe Association and Commisseral Fibers • Connect different areas of the cortex • White matter primarily • Afferent and efferent fibers form the corona radiata – Connecting fibers between cortex and other central structures • Brain stem • Spinal cord • Fibers converge and form: – Internal Capsule • Between thalamus, caudate nuculeus, and lentiform nuclei • Commissures (connect) – Corpus callosum – Anterior commissure – Hippocampal commissure White matter fibers from the cortex 24 Medullary Centers • Interhemispheric (between) Connections • Intrahemispheric (within) Connections • Three types of fibers – Projection: Project through internal capsule – Association: Within a hemisphere i.e. Arcuate fasciculus – Commissural: Between hemispheres i.e. Corpus callosum 25 Major Fissure of the Brain • Longitudinal Fissure – Separates Two Hemispheres of the Brain – Aka ‘Interhemispheric Fissure’ • Falx Cerebri resides here – Superior sagittal sinus – Inferior sagittal sinus 26 Major Folds of the Brain • The folds of your brain are like a fingerprint – there are a few general patterns, with individual variability. • Two main folds – Central Sulcus Fissure of Rolando Rolandic sulcus – Lateral sulcus Sylvian fissure The central sulcus separates the frontal and parietal lobes. The lateral sulcus separates the temporal lobe from frontal, parietal, insula 27 The major cortical lobes Insular Lobe – Tucked away, but often injured in patients seen by speech pathologists 28 Major Medial Sulci Central Sulcus Parieto-occipital Sulcus Calcarine Sulcus Preoccipital Notch 29 Lobes et al of the Brain 30 Landmarks of the frontal lobe • • • • • • Frontal Pole Precentral Gyrus Precentral Sulcus Premotor Cortex Speech, Fine Motor Prefrontal Cortex 31 Frontal Lobe Functions • Motor Function • Cognitive Functions • Reasoning, Abstract Thinking, SelfMonitoring, Decision Making, Planning, Inhibition • Organization of Spoken Language Frontal Motoric Areas 32 Frontal Lobe • Cognition of motor intentions – Input from Parietal tactile & visuospatial areas – Active when one sees, feels, senses object and reaches for it – Movement for identity of unseen but felt object – Projects to reticulospinal tract nuclei in brainstem Broca Area – speech production Expressive speech Pars triangularis (Inferior fronal gyrus) Pars orbitalis (Inferior frontal gyrus) Pars opercularis (Inferior frontal gyrus) 34 Prefrontal Cortex • • • • • • • • • Reasoning and judgment Abstract thinking Decision making Social behavior Important in conscious learning Connects movement to behavior Engaged in “working memory” Involved in realization of consequence Well connected to the limbic system Parietal Lobe Landmarks • Post Central Gyrus (PoCG) – Primary Sensory Cortex • Superior and Inferior Parietal Lobules (SPL, AnG,SmG) – Perceptual Synthesis, Spatial Orientation, Memory • Angular Gyrus (AnG) Supramarginal Gyrus (SMG) – In Dominant Hemisphere: Reading, Writing and Calculation 36 Parietal Lobe • BA’s #3,1 & 2 = Primary Somatosensory Cortex – Tactile and visuospatial • • • • • • Somatosensory association Body awareness Stereognosis Physical & functional identification of objects In infant, this area requires continuous stimulation Important area Chiropractically The homunculus (little man) • The motor strip (red, frontal cortex) and primary sensory cortex (green, parietal) spatially map corresponding portions of the contralateral hemisphere. 38 Humunculi London Natural History Museum Sensory and Motor Humunculae: Notice the difference in the hands, feet, trunk and tongue. Temporal Lobe – Major External Gyri • Superior Temporal Gyrus • Middle Temporal Gyrus • Inferior Temporal Gyri Temporal Pole 41 Temporal Lobe • • • • Olfactory processing Auditory Processing Memory Processing Wernicke’s area – (BA22) in left lobe – Pathology causes nonsense speech http://www.stroke.org.uk/research/new-research-post-stroke-aphasia Temporal Operculum • Dorsal surface of STG is called the ‘Temporal Operculum’ (Lip) – Middle section: Heschel’s Gyri (Brodmann Areas 41 + 42) • Auditory Reception Cortex – Posterior section: Wernicke’s Area (Brodmann 22) • Auditory Association Cortex Heschl’s Gyrus • Primary auditory cortex found in Heschl’s gyrus • This is organized tonotopically – a high pitched sound excites a different region than low pitched sounds. 44 Superior Temporal Gyrus • Auditory Cortex lies inside the Superior Temporal Sulcus • Part of the superior temporal gyrus that is planum temporale imperative for the (nonprimary AC) Heschl’s gyrus perception of speech is (primary AC) Heschl’s gyrus planum polare (nonprimary AC) Ventral-Medial Structures • Temporal Lobe – Fusiform gyrys (Face Recognition) – Hippocampal Gyrus (places, memory) – Uncus (smell) • Occipital lobe – Cuneus and Lingual gyrus (primary vision) 46 Medial View Hippocampal Formation • Located in each temporal lobe (bilateral) • Part of the limbic system • Involved in – – – – memory and learning Hypoglycemia Anoxia Status epilepticus (lots of damage seen here) • Primary afferent supply is entorhinal cortex – Smell • Grows as for as long as learning continues Ventral-Medial Structures Uncus Parahippocampal Gyrus Fusiform Gyrus Lingual Gyrus Cerebellum and Brainstem removed 48 Occipital Lobe • Occipital Pole (medial) – Medially: cuneus and lingual gyrus: primary visual cortex – Clinically: field cuts, blindsight • Lateral occipital structures: – Superior, Lateral and Superior Occipital Gyris: Secondary Visual Cortex (Association) 49 Occipital Lobe • Visual center of the brain – Conscious vision – Interprets, associates, and facilitates visual images and connects to • Contralateral hemisphere, prefrontal cortex, parietal lobe – Each side receives input from contralateral retina Language Areas 51 Insular Lobe (Isle of Reil) • Deep in Lateral Fissure – Functions: Language(?), taste, disgust, cravings (e.g. smoking) Insula (Isle of Rile) • 5th lobe of the cerebral cortex • In the lateral cerebral fissure • Communicates with frontal and parietal lobes – Visceral sensory and motor and somatosensory and somatomotor functions • • • • Gastrointestinal and cardiac regulatory functions Motor association area Memory to language Olfactory gustatory correlation Midsagittal Surface • Corpus Callosum – Connects Hemispheres • Limbic System – Emotions • • • • Cingulate Gyrus Fornix Thalamus Hypothalamus 54 Cingulate Cortex • Part of the limbic system • Surrounds the corpus callosum • Input from – itself bilaterally – Anterior thalamic nuclei – Temporal lobe • Part of circuit of Papez – (see later slide) Circuit of Papez • hippocampal formation (subiculum) → • fornix → • mammillary bodies → • mammillothalamic tract → • anterior thalamic nucleus→ • cingulum → • entorhinal cortex → • hippocampal formation • http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Papez_circuit • Used with permission from James Montgomery http://montgomeryillustration.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/04/Papez.jpg Striatum Head of Caudate Nucleus Cleft for Internal Capsule Thalmus Putamen Amygdaloid Nucleus Tail of Caudate Nucleus 57 Lateral View Midsagittal Surface Corpus Callosum Cingulate Gyrus Septum Uncus Fornix 58 Transverse Slice Fornix Claustrum Putamen Caudate Nucleus Thalamus Globus Pallidus 59 Basal Ganglia • • • • Caudate Nucleus Putamen Globus Pallidus (Pallidum) Caudate Nucleus +Putamen = Striatum • Putamen + Globus Pallidus = Lenticular Nucleus 60 Brain Stem Optic Nerve Midbrain Pons Medulla Optic Chiasm Optic Tract Pes Pedunculi Pituitary Stalk 61 Infant brain stem • At birth, the most developed area of the brain is the brain stem. • This controls the involuntary reflexes: crying, rooting, sucking, grasping, stepping, etc. • The Medulla controls the vital life funcctions: breathing, heart rate, blood pressure, and sleep • Brainstem also handles some of the babies emotions: like anxiety and calming Midbrain, Hindbrain • Pons • Medulla Oblongata • Functions: Automatic Control Systems 63 Ventral Brainstem • • • • • Mamillary Bodies Medial Sulcus Ventral Median Fissure Pyramidal Tract Pyramidal Decussation – Where signals cross • Ventral lateral sulcus 64 Midbrain Dorsal Structures • Superior and Inferior Colliculus Dorsal View of Brainstem – The ‘little hills’. – Superior colliculi – help Pineal Body initiate eye movements, integrate visual, auditory Colliculus and tactile information Superior – Inferior colliculi- audition • Aka Corpora Quadrigemina (four seeds) Inferior Brachium Superior Colliculus Inferior Colliculus Trochlear Nerve 65 Cranial Nerves at Brainstem http://web.uni-plovdiv.bg/stu1104541018/docs/res/anatomy_atlas_-_Patrick_W._Tank/7%20-%20The%20Head%20and%20Neck_files/C7FF55.jpg 66 Colliculi • Superior colliculi: eye movement control. Also maps touch and hearing onto vision • Inferior colliculi: pathway for auditory processing Note proximityof the colliculi and brainstem structures to the 4th ventricle Sagittal View Internal Structures of the Midbrain • • • • • • Tegmentum Cerebral Aqueduct Red Nucleus Cranial nerve nuclei Reticular Formation Central Gray Area Transverse Section of Rostral Midbrain Tectum Tegmentum Basis Pedunculi 68 Internal structures of the pons • Tegmentum – Ascending and Descending Fibers – Medial Lemniscus • Basilar Pons – Cortical Descending Tracts – Pontine Nuclei – Pontocerebellar Fibers Transverse Section of Mid Pons Tegmentum Basilar 69 Medulla Oblongata • Connects to Pontine Protrusion • Caudal Portion Contains Pyramidal Decussation • Where motor tracts cross over for control of contralateral side of the body Tegmentum Pyramid 70 Landmarks of Medulla • Ventral – Ventrolateral Sulcus – Pyramidal Tract – Lateral Corticospinal Motor Tract • Dorsal – Dorsal Median Sulcus – Dorsolateral Sulcus – Olivary Nucleus 71 Internal Medulla • Dorsal Tegmentum • Ventral Pyramidal Tract • Reticular Formation – Cardiac Center – Vasomotor Center – Respiratory Center 72 Cerebellum • Modifies Cortical Activity • Distinctive Appearance – Gyri called Folia – Two Hemispheres • Three Lobes – Anterior – Posterior – Flocculonodular 73 Cerebellum Posterior lobe • Rostral view – (bird’s eye) Anterior lobe 74 Cerebellum • Caudal view (from the feet) Posterior lobe Anterior lobe 75 Flocculus Cerebellum • Anterior view Flocculus Nodulus 76 Cerebellum • Midsagittal slice Vermis Nodulus Flocculus 77 Spinal Cord • Same Meningeal Layers as the Brain • About 45cm long • Diameter of 1 cm. Root filaments Dorsal Ventral Pia mater Arachnoid mater Mixed spinal nerve Dura mater 78 Spinal Nerve Components • Dorsal Division: sensory part of nerve, sensory information enters spinal cord through dorsal root fibers • Ganglion: cell bodies of these nerves come together to create the dorsal root ganglion • Dorsal Horn or Column: information enters the spinal column at the dorsal horn Spinal Nerve Components • Ventral Division: motor commands, leave the ventral root and go to muscles • Ventral Horn or Column: information passed from brain to spinal cord then from the ventral root to the extremities Transverse view of spinal cord "Copyright © 2005 by Thompson Delmar Learning, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED" Segmental Spinal Reflex Arc • • A stimulus/response system that maintains a constant state of muscular tone Works by: – muscles spindles sense stretching and send information through gamma nerves to dorsal root of spinal cord – a signal is sent back from the ventral root for the muscle to contract Spinal Cord • Dorsal root fibers form ganglion • Connect to ventral fibers to form peripheral spinal nerves. • Attached by Filum Terminale 83 Internal Spinal Cord • • • • • • Gray Matter Two Dorsal Horns (Sensory Info) Two Ventral Horns (Motor Info) White Matter Three Myelinated Fasciculi Dorsal, Lateral and Ventral 84 Spinal Cord Segments & Nerves 31 Spinal Segments and Nerves Cervical 8 Lumbar 5 Thoracic 12 Coccygeal 1 Sacral 5 85 Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) • 12 pairs of cranial nerves– Sensory, motor, or mixed “On Old Olympus Towering Top A Famous Vocal German Viewed Some Hops.” • 31 pairs of spinal nerves Divisions of the PNS • Somatic Nervous System (under voluntary control) – Sensory and Motor – Skin and Muscles • Autonomic Nervous System (can not be voluntarily controlled). – – – – Sensory and Motor Visceral organs and glands Two main subdivisions: Sympathetic: Fight, Flight, Fear • Prepare to expend energy – Parasympathetic: Regulates normal function • Prepare to conserve energy 87 Cranial Nerves (12 pair) I. II. III. IV. V. Olfactory: sensory for smell Optic: sensory for vision Oculomotor: motor for vision Trochlear: motor for vision Trigeminal: sensory to eyes, nose, face and meningies; motor to muscles of mastication and tongue Cranial Nerves VI. Abducen: motor to lateral eye muscles VII. Facial: sensory to tongue and soft palate, motor to muscles of the face and stapes VIII. Vestibulocochlear: sensory for hearing and balance (aka Acoustic) IX. Glossopharyngeal: sensory to tongue, pharynx, and soft palate; motor to muscles of the the pharynx and stylopharyngeus Cranial Nerves X. Vagus Nerve: sensory to ear, pharynx, larynx, and viscera; motor to pharynx, larynx, tongue, and smooth muscles of the viscera, 2 parts: superior laryngeal branch and recurrent laryngeal branch XI. Spinal Accessory Nerve: motor to pharynx, larynx, soft palate and neck XII. Hypoglossal Nerve: motor to strap muscles of the neck, intrinsic and extrinsic muscles of the tongue