* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Islam and Sikhism wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Mormonism wikipedia , lookup
Islam and violence wikipedia , lookup
Islam and modernity wikipedia , lookup
Islam and secularism wikipedia , lookup
Islam and war wikipedia , lookup
Sources of sharia wikipedia , lookup
Imamah (Shia) wikipedia , lookup
Political aspects of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of Twelver Shia Islam wikipedia , lookup
Morality in Islam wikipedia , lookup
Soviet Orientalist studies in Islam wikipedia , lookup
Muhammad and the Bible wikipedia , lookup
Satanic Verses wikipedia , lookup
Islamic culture wikipedia , lookup
Succession to Muhammad wikipedia , lookup
Islam and other religions wikipedia , lookup
Abbasid Caliphate wikipedia , lookup
History of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islamic schools and branches wikipedia , lookup
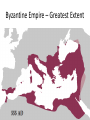
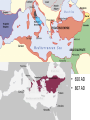
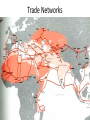
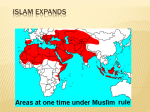
Expansion of Islam Setting the Stage • Muhammad dies in 632 • Religion in crisis – No leader • Is this a problem? If so, what issues might appear? Successors • Muhammad had not named a successor • Following customs, AbuBakr becomes the 1st caliph (“successor” or “deputy”) • “Rightly Guided” Caliphs – Umar, Uthman, & Ali – knew Muhammad • Use the Qur’an & Muhammad’s teachings to lead = the Caliphate Initial Problems & Expansion • Tribes abandon Islam, refuse to pay taxes, & some declare themselves prophets • Abu-Bakr invokes jihad (“striving”) – Two Meanings • By Abu-Bakr’s death in 634 – all of Arabia controlled • Umar & Ali – fight the Byzantines and Sassanids expanding empire from the Atlantic to the Indus River Byzantine Empire – Greatest Extent • 650 AD • 867 AD Reasons for Success • These caliphs are successful because they follow Muhammad’s teachings • Muslims view expansion as full support from Allah = fight to defend Islam • Armies are disciplined & have great commanders • Use the weaknesses of the Byzantines & Sassanids to expand – Empires crumbling – Harsh treatment of peoples – Islam offers equality Conquered Peoples • Qur’an forbids forced conversion • Conquered peoples allowed to practice their own religion • Jews & Christians receive special considerations – why? • Some restrictions: no spreading of religion, pay a special poll tax • Could be officials, bureaucrats, & scholars Internal Conflict • 656 – Uthman murdered = civil war • Ali (natural successor) is challenged by Muawiya of Syria – Assassinated in 661 • Elective system dies with him – why? • Umayyads take control – move capital to Damascus • Abandon simple life – surround themselves with wealth • Will cause division – why? Sunni – Shi’a Split • Majority of Muslims side with Umayyads • Minority resist – caliph needs to be a descendant of the Prophet – Shi’a – “party” of Ali • Ummayyads = Sunnis (Follow Muhammad’s example) • Sufi – Life of poverty & devotion Change in Power • 750 – Umayyads overthrown by the Abbasids – Murder remaining Umayyads • Abd al-Rahman flees to Spain, sets up Umayyad caliphate • Leads Berber army north until defeat at the Battle of Tours in 732 • From state in al-Andalus in Southern Spain Abbasid Power • 762 – move capital to Baghdad – consolidate power • Located on key trade & communication networks • Strong bureaucracy – treasury, defense, & business departments • Send diplomats to take care of affairs • Tax land, imports, exports, & non-Muslim wealth to maintain rule Independent Rivals • Abbasid power was strong, but rivals spring up • Independent states dominate small regions all across their land • The Fatimid - descendents of Fatima (Muhammad’s daughter) – North Africa – Trade, religion, & language connect them to the Abbasids Trade Networks • Sea Trade: Red & Mediterranean Seas = trade with the rest of the world • Land Trade: Silk Road – China – Middle East – Europe & Africa • Only one language & one currency – Today? • Banks set-up with credit (sakks) – European origin? • Cities explode & become centers for the arts, science, & achievements The Silk Road Trade Networks