* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Rise of Spread of Islam
The Jewel of Medina wikipedia , lookup
Imamah (Shia) wikipedia , lookup
Islamic Golden Age wikipedia , lookup
Satanic Verses wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of Islamism wikipedia , lookup
Sources of sharia wikipedia , lookup
War against Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islamic democracy wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of Twelver Shia Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Sikhism wikipedia , lookup
Islam and violence wikipedia , lookup
Spread of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islamic ethics wikipedia , lookup
Succession to Muhammad wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Afghanistan wikipedia , lookup
Historicity of Muhammad wikipedia , lookup
Soviet Orientalist studies in Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam and war wikipedia , lookup
Morality in Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam and secularism wikipedia , lookup
Islamic missionary activity wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Bangladesh wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Indonesia wikipedia , lookup
Islam and modernity wikipedia , lookup
History of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islamic culture wikipedia , lookup
Political aspects of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Schools of Islamic theology wikipedia , lookup
Islam and other religions wikipedia , lookup
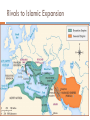
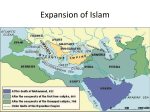
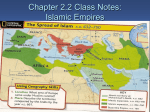
THE RISE OF SPREAD OF ISLAM Chapter Six AP World History Ms. Tully The PostClassical Period: Faith and Commerce Spread of major world religion Development of systematic international trade Three Big Concepts Pre-Islamic Arabia Bedouin culture based on kin/clan/tribal networks Shayks – clan/tribal leaders Fierce interclan rivalries and struggles for resources Towns and long-distance trade Mecca & Medina Pre-Islamic Arabia Status of women varied by clan Little art/architecture – focus on poetry Bedouin religions – blend of animism & polytheism The Life of Muhammad & Gensis of Islam Born around 570 CE Merchant, married Khadijah One of many prophets concerned about life in Arabia 610 CE – Muhammad receives revelations from angel Gabriel Qu’ran basis of new religion The Fight for Islam in Arabia Umayyads in Mecca saw Muhammad as a threat Muhammad flees to Medina Hijra 620s – Conflict between Muhammad’s Median forces & Umayyad controlled Mecca Destroyed old idols, Mecca now under Islamic faith The Appeal of Islam Monotheism dominated any tribal or class divisions Umma – Community of the faithful Provided ethical system Qu’ran Similarity/unity with other Semitic religions The Appeal of Islam Five Pillars of Islam Profession of faith Pray 5x day Fast during Ramadan Pay Zakat for charity Perform a Hajj Muhammad’s Successor? Died in 632 – who should succeed him? Creation of Caliph – political and religious successor to Muhammad Ali – Muhammad’s son-inlaw? Abu Bakr – Muhammad’s close friend Ridda Wars military campaigns against rebel Arab clans Spread of Islam New sense of unity & strength Booty came from conquests Jihad theory of conquest not true Sasanian empire weak overthrown by 651 Byzantines weakened by Arabs, but not destroyed Rise of naval supremacy Rivals to Islamic Expansion Spread of Islam The Sunni-Shi’a Split The main division between Sunni and Shia Muslims is originally not a religious one, but a political one. Sunni Muslims: Abu Bakr was the best choice as caliph; caliphs should be chosen from the umma (Muslim community). (85%) Shia Muslims: Ali should have been picked as caliph (successor should have been kept in the family). They do not recognize the authority of Sunni Muslim leaders. (15%) Over centuries, differences in belief and law develop which contributes to many major disputes in the region until this day Geographic Distribution of Sunni/Shi’a Caliphs & Caliphates Caliph = Islamic religious and political leader Caliphate = dynasty of Islamic caliphs Rashidun or Rightly Guided Caliphs (632-661) Abu Bakr; Umar; Uthman; Ali Umayyads (661-750, centered in Damascus) Abbasids (750-1258, centered in Baghdad) Córdobas (756-1031, Iberia) Fatimids (909-1171, North Africa, Shi’a) Almohads (1145-1269, North Africa, Iberia) Ottomans (1517-1922) Umayyad Caliphate Political center moved to Damascus Small Arab & Muslim aristocracy ruled over empire of nonArabs/Muslims Mawali – Non-Arab Muslim converts Dhimmi – people of the book Umayyad Caliphate New expectations for women & marriage Umayyads addicted to luxury – big reason for downfall Revolts in empire began in 740 CE Rise of Abbasid challenge Abbasid defeated Umayyads in 750 hunted down all members of Umayyad family ‘Abd al-Rahman escaped formed caliphate in Cordoba Abbasid Caliphate Moved capital to Baghdad Bureaucratization of empire Wazier Full integration of converts Rise in the status of merchants Growth of cities Translation and preservations of classical texts Key to development of great trade routes