* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 10.2 The Spread of Islam
Succession to Muhammad wikipedia , lookup
Reception of Islam in Early Modern Europe wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Mormonism wikipedia , lookup
International reactions to Fitna wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of Islamism wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of Twelver Shia Islam wikipedia , lookup
Satanic Verses wikipedia , lookup
Islam and violence wikipedia , lookup
Sources of sharia wikipedia , lookup
Muhammad and the Bible wikipedia , lookup
Islamic extremism in the 20th-century Egypt wikipedia , lookup
Islam and war wikipedia , lookup
Islamic–Jewish relations wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Somalia wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Afghanistan wikipedia , lookup
Soviet Orientalist studies in Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Sikhism wikipedia , lookup
Islam and secularism wikipedia , lookup
Morality in Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam and modernity wikipedia , lookup
War against Islam wikipedia , lookup
Spread of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Indonesia wikipedia , lookup
Historicity of Muhammad wikipedia , lookup
Islamic missionary activity wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Bangladesh wikipedia , lookup
History of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Political aspects of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islamic culture wikipedia , lookup
Schools of Islamic theology wikipedia , lookup
Origin of Shia Islam wikipedia , lookup
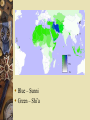
10.2 The Spread of Islam Forging a religious empire despite internal conflict. Muhammad’s Successors After Muhammad’s death in 632, AbuBakr becomes the 1st caliph or successor/deputy to the head of Islam. The reign of a caliph was known as a caliphate. Example: Caliph Abu-Bakr • During caliphate of Abu-Bakr, there were many uprisings that were quickly subdued (put down). “Rightly Guided” Caliphs Called “rightly guided” because they used the Qur’an and Muhammad’s actions as guides. Used military force to stop rebellions within Islam and eventually use armies to spread Islam to Syria and lower Egypt Muslims see military victories as a sign of Allah’s support of Islam. Islam Conquers Empires Byzantine and Persian Empires fall because of – Weakness – Religious persecution – Those persecuted welcomed invaders Treatment of Conquered Peoples Many people attracted by Islam’s message and accept Islam. Qur’an forbids forced conversion so, many retain their own religions, but had to pay a poll tax so they don’t have to serve in the army. Christians and Jews can practice, but not spread their religions. Internal Conflict ~ Crisis Uthman and Ali assassinated and the system of choosing a caliph is gone. Umayyads – family that gains power of caliphs and move Muslim capital. Unpopular: – Move capital from Mecca to Damascus - too far from Muslim homeland – Abandon simple life for life of luxury The Sunni and the Shi’a Split Shi’a – The party or followers of the Prophet Muhammad: – Caliph must be a relative of Muhammad Sunni – Believe that the first four caliphs (not related to Muhammad) are rightful successors to Islam. – Caliph must follow Muhammad’s example Blue – Sunni Green – Shi’a Conflicts “Resolve” Abbasids overthrow Umayyads in 750 Prince Abd alRahman escapes to Spain to help form Muslim state in Spain. – “rock” Jabal Tariq ~ Gibraltar Conflicts “Resolve” cont... Abbasids move capital to Baghdad. Muslim empire flourishes Abbasid caliphate lasts 750-1258 Rival groups split Muslim lands – Fatmid Dynasty – named after Fatima (Muhammad’s daughter) – Empire breaks up as independent states gain independence Muslim Trade Oceans enable trade – Med & Indian Land enables trade – Silk Roads link China and India to Europe and Africa Muslim merchants need unity: – Language: Arabic – Currency ($): Dinar – Banks create sakks – pronounced “check” Sunni & Shi’a: Religious SECTS Sectarian Violence