* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Immune System Period 1 - Mercer Island School District
Childhood immunizations in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Plant disease resistance wikipedia , lookup
Immunocontraception wikipedia , lookup
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Transmission (medicine) wikipedia , lookup
Globalization and disease wikipedia , lookup
Social immunity wikipedia , lookup
Germ theory of disease wikipedia , lookup
Autoimmunity wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Herd immunity wikipedia , lookup
Vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Sjögren syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Immunosuppressive drug wikipedia , lookup
Sociality and disease transmission wikipedia , lookup
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency wikipedia , lookup
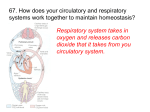
Immune System Period 1 By: Seth, Charlie and Nikhil Your presentation should include: The main function(s) of the body system The main organs (or cell types) of this system and the function of each part At least one example of how this system helps to maintain homeostasis in the body Explanation of how the system works with other systems (some specified below) A description of at least 2 disorders/diseases that can affect this system. Describe how a vaccine works Functions of the different types of white blood cells and proteins involved in immunity Innate vs. Acquired (Adaptive) Immunity At least one immune system disease given should be an autoimmune disorder (include definition of autoimmune disorder). Main Functions -The main function of the Immune system is to protect the body from pathogens and infections. (A pathogen is a disease-causing microorganism) Organs involved - Lymph Nodes: Produce and store white blood cells - Spleen: Contains white blood cells to fight infection. - Bone Marrow: Produces white blood cells - Lymphocytes: B and T cells that - Thymus: Where T-cells mature - Leukocytes: Identify and eliminate pathogens Interactions with other systems The immune system is like a small police force that constantly patrols every organ and tissue in your body. It works closely with the circulatory system for transportation needs and the lymphatic system for production of lymphocytes. Innate vs Acquired immunity Innate Immunity- Immunity to a disease without undergoing an immune response. This immunity is passed on from parents to children. Acquired Immunity- Immunity to a disease that is created after a specific pathogen has infected the body once. This kind of immunity is a reaction so a pathogen can be dealt with easily the next time it enters the body. This is why people can't catch the same disease twice. (The cold and the flu mutate rapidly and if you catch the flu multiple times, you are infected by a different mutation of the same virus.) Vaccines Vaccines are artificial ways to create an acquired immunity. A vaccine introduces small amounts of pathogens to the body (alive or dead depending on the type of vaccine). When the pathogen is introduced, the immune system can quickly and easily destroy the pathogen. But the immune system also remembers the pathogen and it uses memory B cells so it can destroy the pathogen even more quickly and easily the next time it enters the body. Diseases: Leukemia A disease in the bone marrow that causes the marrow to not function properly. Leukemia causes the bone marrow to produce white blood cells that can't develop, preventing them from fighting infections. Then the bone marrow produces more and more white blood cells in an effort to replace the defective cells. But this attempt to help only hurts the body, it uses up lots of extra energy with zero results, depriving the body of the energy it needs to fight the disease. Diseases: HIV Human immunodeficiency virus is a disease that targets the cells of the immune system. It takes over the T cells and uses them for reproduction. This creates more viruses and destroys the cells fighting them. HIV is not deadly on its own, but it leaves the body wide open to a fatal attack from some of the most harmless diseases.