* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Immunology (B)
Survey
Document related concepts
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Complement system wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Immunosuppressive drug wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
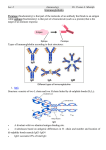
苏州大学《免疫学》E 卷 考试形式 闭卷 院系 ___________ 年级 ____________ 专业 ____________ 学号 ___________ 姓名 ____________ 成绩 ____________ A. Multiple choice questions (1’ * 20) 1. Opsonins include A. perforin B. magainins C. C9 D. C3b E. IFN- 2. Both mast cells and basophils A. are phagocytic B. circulate in the blood stream C. are found primarily in lymph nodes D. have receptors for IgM antibodies E. release histamine 3. Helper T cells are distinguished from cytotoxic T cells by the presence of A. CD2 B. CD4 C. CD3 D. IL-2 receptor E. class II MHC antigen 4. Newborns A. receive IgM antibodies from the mother through placental transfer B. have virtually a full complement of maternal IgG antibodies C. have very few lymphocytes in their circulation D. respond to antigens as well as adults E. receive maternal B cells 5. IgE A. is bound together by J chain B. binds to mast cells through its Fab region C. differs from IgG antibody because of its different H chains D. is present in high concentration in serum 6. IgA A. is present in milk and saliva B. is involved in hay fever C. activates complement by the classical pathway D. crosses the placenta 7. Immunoglobulin light chains A. are joined to heavy chains by peptide bonds B. can be present as both k and l chains as part of a single Ig molecule C. are not found in every major immunoglobulin class D. all have the same amino acid composition E. are present in the Fab fragment of Ig 8. A B cell can express on its cell surface A. membrane IgM and IgD at the same time B. both types of light chain C. secretory component D. IgG that can bind several different unrelated antigens 9. The T cell antigen receptor A. recognizes epitopes on linear peptides associated with MHC determinants B. has Ig light chains C. is made up a heavy chain and 2 microglobulin D. recognizes conformational epitopes on the native antigen Clonal selection A. necessitates that proteins are multideterminant B. requires that each antigen reactive cell have multiple specificities C. involves binding of Ab Fc regions to mast cells D. explains specificity and memory in immunity 11. Th1 cells do not A. express CD4 B. produce IFN- C. activate macrophages D. bind soluble antigen 12. Stimulation of B cells to proliferate and differentiate requires A. B cell immunoglobulin binding of peptide in association with T cell MHC class II B. binding of CD40 on B cells by its ligand on T cells C. IFN- D. B cell surface antibody binding to C3b 13. Stimulation of antigen-specific T cells by appropriately presented antigen alone results in A. induction of cytotoxicity B. production of IL-2 but not other cytokines C. activation resulting in cell division D. anergy 14. Properties of antigen that may influence its role in the induction of tolerance include A. its nature B. its route of administration C. the dose of antigen D. maturity of the immune system E. all of the above 15. Central tolerance takes place in A. lymph nodes B. thymus C. spleen D. liver E. pancreas 16. A major transfusion reaction may occur if the recipient A. has antibodies to transfused cells B. has T cells reactive to blood group antigens C. is RhD compatible E. is AB positive 17. Mast cell products mediate some of the symptoms of immediate hypersensitivity by increasing A. IgE receptors B. secretion of IgE C. capillary leakage D. secretion of IgG 18. Hemolytic disease of the newborn due to RhD incompatibility depends upon the A. mother possessing RhD antigens not present on the baby’s red cells B. inability of the baby to react against the mother’s red cells C. transplacental passage of IgM anti-RhD antibodies D. transplacental passage of IgG anti-RhD antibodies E. production of cytotoxic antibodies by the baby 19. Major histocompatibility antigens are not A. linked with a number of autoimmune diseases B. important for interactions between T and B cells during an immune response C. the only antigens which result in graft rejection D. important for graft versus host reaction 20. Tears contain A. IgA B. IgG C. lysozyme D. all of the above B. Small questions (concept explanation) (5’ * 8 ) 1. primary lymphoid organs 5. TLR 2.Epitope: 6. BCR 3.antibody 7. TAA 4.ADCC 8. Th C. Big questions (10’ * 3) 1. Please explain the definition, functions of complement system and the alternative pathway of complement activation. 2. Please elaborate the history of T cell development and the significance of T cell positive and negative selection. 3.The mechanism of type I hypersensitivity. Immunology (E) answers A. multiple choice questions DEBBC AEAAD DBDEB ACDCD B.small questions (concept explanation) 1. primary lymphoid organs bone marrow where B cell developed and matured thymus comprised by matrix cells and thymus cells. It is where T cells,especially αβ +T cells develop. Interaction between matrix and thymus cells plays an important role in T cell development and maturation. 2.Epitope: Antigen molecules each have a set of antigenic determinants, also called epitopes. Epitopes are molecular shapes recognized by antibodies of the adaptive immune system. 3.antibody antibody is γ- immunoglobulin and antibody is 4-chain structured Y-shaped protein. It is an important components of humoral immunity. Antibody can eliminate pathogens by neutralization, opsoinization, ADCC and activation of Complement. 4.ADCC ANTIBODY-DEPENDENT CELL-MEDIATED CYTOTOXICITY – The linking of antibody bound to target cells (virus infected cells, or some tumor cells) with FcR of natural killer cells (NK cells), neutrophils, macrophages,or eosinophils can result in killing of the target cell. 5. Toll like receptors (TLR) Toll like receptors are a family of proteins of which there are at least 5 known members. Using TLRs, innate immune cells can detect and respond to infection by recognizing conserved motifs of microbes. TLRs transmit signals about microbial constituents to the nucleus, thus regulating the type of genes expressed, and the subsequent response. 6. BCR B cell receptor is membrane-bound immunoglobulin IgM, the function of BCR is to recognize antigen signals and then actives B cells. 7. TAA (tumor associated antigens): are also found on some normal cells. 8. Th Th are CD4+ T cells: TH1: Activate macrophages and cytotoxic T cells to aggressively ingest antigen and to kill ingested microbes. TH2: Stimulate B cells to differentiate into antibody-producing plasma cells. B cells will only undergo isotype switching after receiving T cell help. The Ig class that a B cell switches to is specified by the types and balance of cytokines secreted by the helper T cell. B. big questions 1. Please explain the definition, functions of complement system and the alternative pathway of complement activation. Definition: The complement system is an important component of innate immunity. It can be activated by the classical and alternative pathways, both pathways will eventually lead to the lytic pathway which featured by the formation of MAC. Function of complement: anaphylaxis (C3a,C5a), chemotaxis (C5a) opsonization (C3b,C4b), lysis (C56789) .classical pathway of complement activation Ag-Ab C3 convertase C4b2a a C2b C4b2a3b C5 convertase Classical pathway 45 2. Please elaborate the history of T cell development and the significance of positive and negative selection.The history of T cells. HSC CD4+ CD4+ CD8+ TCR LSC T CD3 Lymphocyte stem cells Bone marrow TCR CD3 Th CD8+ TCR CD3 Tc thymus periphery a) To produce sufficient T cells b) Positive/negative selection: to select T cells that bind weakly/strongly to self MHC molecules. c) Express T CR/CD3 complex positive and negative selection of T cells Positive selection: T cells that express a TCR that can bind weakly to self MHC are spared from death and are positively selected to survive. Negative selection: T cells that react strongly to self-antigens on MHC are eliminated. Only those T cells that can react to MHC, but do not bind strongly to self-antigens emerge as mature T cells from the thymus. 3.The mechanism of type I hypersensitivity. Page 239: introduction, sensitization phase and effector-phase