* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Supplementary Figure Legends
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neural oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Mirror neuron wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Multielectrode array wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Sexually dimorphic nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Pre-Bötzinger complex wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
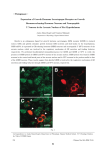
Supplemental Figure Legends SFigure 1: Histopathology of livers from control neurons- or BEP neurons-transplanted groups. A representative liver section from an animal treated with control neurons shows well-differentiated hepatocellular carcinoma with compressed hepatic parenchyma (left). A representative liver section from an animal with BEP neuronal transplants shows almost normal liver morphology with mild fibrosis septae (right). SFigure 2: Representative picture of a back tumor, which developed in some control neuron transplanted animals following intravenous injection of MADB106 cells in female F344 rats. SFigure 3: In vitro release of cAMP at various timepoints from 70 nmol and 350 nmol dbcAMP attached to nanospheres. N =5. SFigure 4: Representative photomicrograph of a section of rat brain showing fluorescently-labeled-nanosphere attached with cAMP (N-cAMP; blue) in the area of 3rd ventricle. Also, showing many green fluorescent-labeled-BEP neurons within the arcuate nucleus. SFigure 5: Effect of nanosphere-delivered dbcAMP (N-cAMP) injection on tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) and corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) levels in the hypothalamus. (A) Representative photograph of the TH staining. (B) Total count of THpositive neurons in the PVN. (C) Representative photograph of the CRH staining. (D) Total count of CRH-positive neurons in the arcuate nucleus. 3V= 3rd ventricle. Data were analyzed using Students’ t-test. * P < 0.05 comparing to control group. N =5.