* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Introduction to Abnormal Psychology and Mental Illness
Bipolar II disorder wikipedia , lookup
Obsessive–compulsive personality disorder wikipedia , lookup
Emil Kraepelin wikipedia , lookup
Victor Skumin wikipedia , lookup
Anxiety disorder wikipedia , lookup
International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems wikipedia , lookup
Excoriation disorder wikipedia , lookup
Anti-psychiatry wikipedia , lookup
Panic disorder wikipedia , lookup
Mental health professional wikipedia , lookup
Bipolar disorder wikipedia , lookup
Moral treatment wikipedia , lookup
Deinstitutionalisation wikipedia , lookup
Factitious disorder imposed on another wikipedia , lookup
Autism spectrum wikipedia , lookup
Psychological evaluation wikipedia , lookup
Depersonalization disorder wikipedia , lookup
Glossary of psychiatry wikipedia , lookup
History of psychiatric institutions wikipedia , lookup
Personality disorder wikipedia , lookup
Emergency psychiatry wikipedia , lookup
Conversion disorder wikipedia , lookup
Mental status examination wikipedia , lookup
Conduct disorder wikipedia , lookup
Separation anxiety disorder wikipedia , lookup
Schizoaffective disorder wikipedia , lookup
Antisocial personality disorder wikipedia , lookup
Asperger syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Generalized anxiety disorder wikipedia , lookup
Controversy surrounding psychiatry wikipedia , lookup
Spectrum disorder wikipedia , lookup
Narcissistic personality disorder wikipedia , lookup
Dissociative identity disorder wikipedia , lookup
Mental disorder wikipedia , lookup
Child psychopathology wikipedia , lookup
Pyotr Gannushkin wikipedia , lookup
Causes of mental disorders wikipedia , lookup
History of psychiatry wikipedia , lookup
Abnormal psychology wikipedia , lookup
Classification of mental disorders wikipedia , lookup
Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders wikipedia , lookup
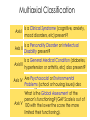
Psychological Disorders and Therapies Abnormal psychology • the scientific study of abnormal behavior in order to describe, predict, explain, and change abnormal patterns of functioning Why should we care? According to the National Institute of Mental Health Statistics: • An estimated 26.2 percent of Americans ages 18 and older — about one in four adults — suffer from a diagnosable mental disorder in a given year. Or 57.7 million people. • About 6 percent, or 1 in 17 —suffer from a serious mental illness. • In addition, mental disorders are the leading cause of disability in the U.S. and Canada for ages 15-44. • Nearly half (45 percent) of those with any mental disorder meet criteria for 2 or more disorders, with severity strongly related to comorbidity. • Most common disorders were anxiety, phobias, and mood disorders Understanding Psychological Disorders John W. Verano Ancient Treatments of psychological disorders include trephination, exorcism, being caged like animals, being beaten, burned, castrated, mutilated, or transfused with animal’s blood. Trephination (boring holes in the skull to remove evil forces) What makes a Behavior a Mental Illness? • The following needs to happen over a relatively long period of time: • “The Four Ds” – – – – Deviance – Different, extreme, unusual Distress – Unpleasant & upsetting Dysfunction – Causes interference with life Danger – Poses risk of harm Theoretical Approaches to Psychological Disorders • Biological approach – Physiological or biochemical basis (medical model) for disorder • Psychological/Psychoanalytical Approach – Thoughts, emotions, the unconscious, personality contribute to disorder • Cognitive-Behavioral Approach – Disorders are the result of learning maladaptive ways of behaving and thinking • Diathesis-Stress Model (part of Biopsychosocial Approach) – Biological predisposition to disorder which is triggered by stress Biological Approach: Medical Model. When physicians discovered that syphilis led to mental disorders, they started using medical models to review the physical causes of these disorders. 1. 2. 3. 4. Etiology: Cause and development of the disorder. Diagnosis: Identifying (symptoms) and distinguishing one disease from another. Treatment: Treating a disorder in a psychiatric hospital. Prognosis: Forecast about the disorder. Classifying Psychological Disorders The American Psychiatric Association rendered a Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM) to describe psychological disorders. The DSM spells out the specific diagnostic criteria • An example of this can be seen in the diagnosis of a major depressive episode. • A person must exhibit at least five or more of the listed nine characteristics and the symptoms must be evident for at least the last two weeks for that person to be diagnosed with this disorder. • When diagnosing a client the American Psychiatric Association recommends that the clinician use a multiaxial Assessment System. Multiaxial Classification Is a Clinical Syndrome (cognitive, anxiety, Axis I mood disorders, etc) present? Is a Personality Disorder or Intellectual Axis II Disability present? Is a General Medical Condition (diabetes, Axis III hypertension or arthritis, etc) also present? Axis IV Are Psychosocial or Environmental Problems (school or housing issues) also present? What is the Global Assessment of the person’s functioning? (GAF Scale is out of Axis V 100 with the lower the score the more limited their functioning). Sample • Axis I 296.21 Major Depressive Disorder 303.90 Alcohol Dependence • Axis II 301.6 Dependent Personality Disorder • Axis III None • Axis IV Recent Divorce, unemployment • Axis V 58 Pros and Cons of DSM Positive: Disorders outlined by DSM-5 are reliable. Therefore, diagnoses by different professionals are similar. FYI: this is not the only diagnostic system. The WHO devised an International Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems (ICD-10). It’s close to the DSM-5, but there are still differences. Negative: Relies too much on social norms and subjective judgments -Too many new categories lead to increase of people diagnosed with a disorder -Prescribing medication seems to be encouraged, where other treatments can be just as effective.