* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cellular Respiration: the details
Lactate dehydrogenase wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrial replacement therapy wikipedia , lookup
Phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Glyceroneogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
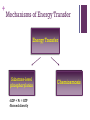
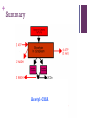
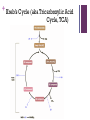
+ Cellular Respiration: the details Miss Tee + 1. 2. 3. 4. + Broken down… not so bad 1. Glycolysis Cytosol (10 steps) 2. Pyruvate oxidation Mitochondrial matrix (1 step) 3. Kreb’s Cycle (TCA, citric acid cycle, CAC) Mitochondrial matrix (8 step cycle) 4. Electron transport chain and chemiosmosis Inner mitochondrial matrix (IMM) + Energy Transfer 1st Law of Thermodynamics Chem potential energy Coupled reactions = efficiency Ultimate goal: capture free energy in the form of _____ Glycolysis only gets energy production started 2.1% of free energy to ATP + Mechanisms of Energy Transfer Energy Transfer Substrate-level phosphorylation -ADP + Pi = ATP -Formed directly Chemiosmosis + Terminology: MVPs Pi= phosphate group ADP, ATP= NAD+= FAD= adenose di/tri phosphate; currency (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide); coenzyme used to shuttle e- to ETC (flavin adenine dinucleotide); coenzyme and e- carrier + Stage 1: Glycolysis Root words? Def: glucose molecule broken down into 2 pyruvate molecules; in cytoplasm 6 carbon sugar 3 carbon sugar + 3 carbon sugar Glucose + Glycolysis Glucose G3P + G3P (precursors for step 2) + Glycolysis G3P Pyruvate + Pyruvate + Glycolysis: balance sheet 2 ATP used 4 ATP produced 2 ATP net + Another perspective… + Review of Mitochondria Structure Specialize in production of +++ ATP: “cell powerhouse” IMM performs functions associated with cell resp Outer membrane Inner membrane (IMM) Cristae Intermembrane space Matrix + Stage 2: Pyruvate Oxidation Glycolysis 2 Pyruvate Transported to IMM + Stage 2: Pyruvate Oxidation 1. CO2 removed 2. 2-carbon oxidized by NAD+ (NAD+ now has potential energy) 3. CoA attached; molecule is prepped for next step + Stage 2: Pyruvate Oxidation Ticket for next step Pyruvate oxidation: 2 pyruvate + 2 NAD+ + 2 CoA 2 acetyl-CoA + 2 NADH + 2 H+ + 2 CO2 + Summary Acetyl-COA + Kreb’s Cycle (aka Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle, TCA) +