* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download action potential presen - Westgate Mennonite Collegiate
Multielectrode array wikipedia , lookup
Patch clamp wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic noise wikipedia , lookup
Spike-and-wave wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Node of Ranvier wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Evoked potential wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Resting potential wikipedia , lookup
Chemical synapse wikipedia , lookup
Action potential wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
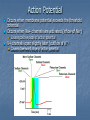
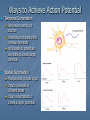
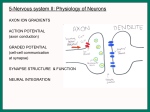
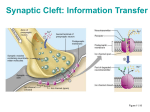
Effects of Excitatory and Inhibitory Potentials on Action Potentials Overview of A Neuron Found in brain, spinal cord and nervous system Electrically excitable Communicate via electrical and chemical synapses Made up of a soma (cell body), dendritic tree and an axon Axon Properties Where action potential is propagated Contains voltage gated sodium and potassium channels Resting membrane potential: ~ -65 mV Action Potential Occurs when membrane potential exceeds the threshold potential Occurs when Na+ channels are activated (inflow of Na+) Causes positive slope of action potential K+ channels open slightly later (outflow of K+) Causes downward slope of action potential Transmission of Action Potential Across Synapse Pre-synaptic cell action potential releases Ca2+ in the axon terminal Axon terminal releases vesicles filled with neurotransmitters Inhibit or help create an action potential Excitatory Neurotransmitters: Acetylcholine glutamate Inhibitory Neurotransmitters: GABA glycine http://thebrain.mcgill.ca/flash/i/i_01/i_01_m/i_01_m_ana/i_01_m_ana. html#2 Post Synaptic Potentials Excitatory Post Synaptic Potentials (EPSP) Creates positive synaptic potential Positive charged ions flow in Allows Na+ into cell Easier for Action Potential to fire Inhibitory Post Synaptic Potentials (IPSP) Decreases the potential of the membrane Increases permeability of K+ K+ flows out of cell Decreases the chances of an action potential Ways to Achieve Action Potential Temporal Summation One neuron acting on another Potential starts before the previous one ends Amplitudes of potentials summate to create larger potential Spatial Summation Multiple cells provide input Input is received in different areas Input is summated to create a larger potential Observations Increasing the intensity does not increase the size of the action potential Action potential is “all or none” response Potentials can summate to elicit or inhibit an action potential Must reach a specific threshold potential to create and action potential that will be propagated Conclusion Many different ways to elicit an action potential or to inhibit one Temporal and Spatial Summation allow for greater complexity in neural networks This allows for greater complexity in organisms neuron can communicate with multiple neurons > greater efficiency.