* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PPT
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Affective neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Human multitasking wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
Emotional lateralization wikipedia , lookup
Types of artificial neural networks wikipedia , lookup
Neural modeling fields wikipedia , lookup
Cortical cooling wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Multielectrode array wikipedia , lookup
Binding problem wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Functional magnetic resonance imaging wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Brain–computer interface wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Neural oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neural binding wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Neuroprosthetics wikipedia , lookup
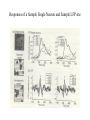
Ch.14 Using Spikes and Local Field Potentials to Reveal Computational Networks in Monkey Cortex KRISTINA J. NIELSEN AND GREGOR RAINER 2009. 01. 13. Tue. Shin Won-jin Contents • Introduction • Measures of neural activity – At the level of neurons – At the level of networks • Previous work on LFP and SUA/MUA – Similarities btw LFP & SUA/MUA – Differences btw LFP & SUA/MUA • Combining LFP to SUA – To reveal computational networks across the brain Introduction • Traditional neurophysiology: Singe-Unit Activity(SUA) – To uncover the neural basis of cognition and action – Ex) sensory systems, motor system • Recent neurophysiology: Local Field Potential(LFP) – A signal that reflects aggregate activity across populations of neurons near the tip of the microelectrode • SUA+LFP offers better insight into cortical brain mechanisms Measures of Single Neural Activity(SUA) 1. Amplify and collect the comprehensive broadband electrical signal – Using microelectrodes 2. Digitize at rate of 20kHz or higher 3. High-pass filtering to remove low-frequency components 4. Clustering to extract the times of action potentials - High frequency band -400Hz~3kHz -MUA -Low frequency band -0Hz~300Hz -LFP MUA/SUA and LFP • MUA(Multi-unit activity) – Weighted average of the spiking activity within a sphere of about 200~300µm around the electrode tip • c.f.) SUA(Single-unit activity) – Represent local processing within a cortical column as well as the long-range output that targets distant brain regions • LFP – Weighted average of the synaptic signals of a neuronal population within 0.5~3mm of the electrode tip – A measure of the local processing in a brain region as well as of the inputs that the brain region receives Similarities btw MUA/SUA and LFP(1/2) • Similarities btw MUA/SUA and LFP – In area V1, the initial cortical stage of visual processing • Sensitive to the orientation of a grating pattern, as well as grating’s contrast(LFP, SUA) – In area MT, the visual cortex of motion perception • Preferences for particular stimulus speeds and motion directions(LFP, MUA) • Performance in a speed discrimination task(LFP, MUA) – Inferotemporal(IT) cortex, final stage of ventral visual processing system • Selectivity for complex objects(LFP, SUA) • Tolerance to changes in an object’s position in space, as well as the object’s size(LFP, SUA) Similarities btw MUA/SUA and LFP(2/2) • In M1 & SMA, primary & supplementary motor area – Information about arm movements(LFP) – Direction of an arm movement Which hand is used for a task Whether the monkey moves only one or both hands(SUA) • In PRR & LIP in the posterior parietal cortex – Maps for the direction of either arm or eye movements that the monkey is intending to perform(SUA) – Direction of planned arm and eye movements(LFP) – Tuning widths for movement directions(LFP, SUA) LFP in general shows responses properties similar to that of the neurons recorded in the same brain region Differences btw LFP & MUA/SUA(1/4) • LFP pools signals over a larger neuronal population than the other two signals – Neurons contributing to the LFP signals have more diverse response properties the ones contributing to either SUA or MUA – Ex) LFP is a poor predictor of the behavior of single neurons LFP correlates better w/ the average signal of the neuronal population Agreement in stimulus selectivity btw single neurons and the LFP signals recorded at the same electrode Differences btw LFP & MUA/SUA(2/4) • Some results cannot be explained by the previous assumption – LFP is an average over a larger neuronal population than MUA/SUA – Ex) About 20% of the LFP site in MT are not visually responsive Almost all MUA sites respond visually • Local three-dimensional structure of cortex Different sources generating LFP and SUA/MUA Combined analyses of these signals Differences btw LFP & MUA/SUA(3/4) • In area V1 – SUA/MUA show strong adaptation effect – LFP response remains elevated throughout the presentation duration • In area M1 & SMA – Correlation btw LFP and SUA is absent in one brain area but present in another • In the motor cortex, of predicting monkey behavior – LFP can be used to successfully decode a movement direction – About 50ms after this is possible based on SUA/MUA – LFP+SUA/MUA results in higher decoding accuracy Differences btw LFP & MUA/SUA(4/4) • In LIP – SUA & LFP can be used to predict the direction of an eye movement – Only LFP can be used to decode the transition from planning an eye movement to executing it • In PRR – SUA predict the direction of an eye or arm movement – LFP distinguish btw eye and arm movement Summary of Previous Works on SUA/MUA & LFP • LFP & SUA/MUA reflect different brain processes – LFP reflects input and local processing to a brain region – SUA/MUA represent the output of that region • Similarities – High degree of similarity btw the inputs to a brain region and it outputs • Discrepancies – Instances where input and output are not closely related Combined analysis of LFP and SUA/MUA has the power to reveal how different brain regions interact with each other to process information Combining LFP to SUA • Two monkeys were trained to discriminate btw natural scenes • Determined the regions of each natural scene on which the monkeys relied to perform the discrimination task • Constructed unique stimulus sets for each monkey – Diagnostic scene regions + 3 modifications – Non-diagnostic scene regions + 3 modifications • Probe the influence of diagnosticity on the responses of single neurons and the LFP in the IT cortex Responses of a Sample Single Neuron and Sample LFP site Influence of Recording Position