* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lesson 1 DNA and proteins
Frameshift mutation wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
DNA polymerase wikipedia , lookup
Bisulfite sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
History of RNA biology wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Human genome wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
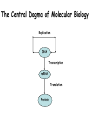
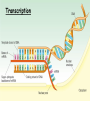
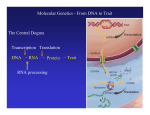
DNA and proteins • State that genes code for polypeptides including enzymes. • Explain the meaning of the term genetic code. • Describe, with the aid of diagrams, the way in which a nucleotide sequence codes for the amino acid sequence in a polypeptide. Starter • In your allocated pairs draw a mind map to link the following key terms: • Allele, base sequence, Chromosome, DNA, Gene, Genetic code, mRNA, Nucleus, Nuclear pore, Protein, Ribosome, RNA, The genetic code • Polypeptides are chains of amino acid residues joined by peptide bonds. • There are 20 different aa and their sequence determines the structure and function of the protein. • The sequence of bases in a DNA molecule determines the sequence of aa. • A gene is a length of DNA that codes for one (or more) polypeptides. • A genome is the entire sequence of DNA of an organism (about 25000 genes in the human genome). • Each gene occupies a specific locus (position) on a chromosome and each chromosome consists of one molecule of DNA. • The DNA is wrapped around basic histone proteins (Chromatin) • In between genes is non coding DNA • Several genes that function together are called a cistron Genes code for polypeptides such as: Structural proteins (keratin, collagen, actin, myosin) Enzymes electron carriers Haemoglobin Antigens, immunoglobulins Cell surface receptors Channel proteins The Genetic Code Features of the Genetic Code • • • • • It is a triplet code It is degenerate It has punctuation It is widespread but not universal It is a non overlapping code The genetic Code The Central Dogma of Molecular Biology Replication DNA Transcription mRNA Translation Protein Principles of Protein synthesis • • DNA stays in the nucleus Proteins are made on ribosomes in the cytoplasm SO • • The genetic code must be copied to messenger RNA (mRNA) mRNA leaves the nucleus via the nuclear pores taking the code to the ribosomes Gene expression occurs in two steps 1. Transcription – the code on part of a DNA molecule is copied to a mRNA molecule. 2.Translation – the mRNA takes the code to a ribosome where it is used to make a polypeptide. Transcription • The process by which the base sequence of a gene is converted into a complimentary base sequence of mRNA • One strand of the DNA (template strand) is used to make mRNA the other stand is the coding strand. • Only part of a DNA molecule is transcribed at one time. Transcription Transcription • The part of the DNA molecule to be transcribed unwinds and ‘unzips’ as DNA helicase breaks the H bonds between the bases • RNA polymerase catalyses the binding of activated free RNA nucleotides to the template • Uracil binds to adenine NOT thymine • The nucleotides condense together forming phosphodiester bonds • The mRNA is complimentary to the template strand and a copy of the coding strand mRNA and the Genetic Code