* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Complementary base pairing Hydrogen bonding between purines
Maurice Wilkins wikipedia , lookup
Bottromycin wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
Community fingerprinting wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
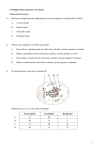
Complementary base pairing Hydrogenbondingbetweenpurines(AandG)andpyrimidines(TandC)inDNA DNA helicase AnenzymethatunwindsandunzipsthedoublestrandedDNAbybreakingthe weakhydrogenbondsbetweenthepairedbases AnenzymethatpositionsandjoinsnewcomplementaryDNAnucleotidesinto placeduringDNAreplication Amolecularcomplexofthreesubunits;phosphate,apentosesugaranda nitrogen-containingbase ContainsDNAfromtwoormoredifferentsources TheprocessofcopyingoneDNAdoublehelixintotwoidenticaldoublehelices AtermreferringtothefactthatafterDNAreplication,anewdoublehelixhas oneconservedold“template”strandandonenewstrand DNA polymerase nucleotide recombinant DNA replication semi-conservative replication amino acid anti-codon codon Anorganicmoleculecomposedofanaminogroupandanacidicgroup AtripletofthreebasescomplementarytoacodonofmRNA AtripletofnucleotidesinmRNAthateithercodesforaparticularaminoacidor signalspolypeptidetermination DNA sequence (genetic code) a succession of letters (ACTG) that indicate the order of nucleotides within a DNA molecule. elongation Secondstepofproteinsynthesis,inwhichapolypeptideincreasesinlengthone aminoacidatatime environmental mutagen Environmentalinfluencescausingmutationsinhumans genetic disorder Anillnesscausedbyoneormoreabnormalitiesinthegenomeeg.sicsickleeg. Sicklecellanemiaiscausedbyapointmutation initiation Firststepofproteinsynthesis,inwhichallthetranslationcomponentsare broughttogether messenger RNA (mRNA) AribonucleicacidmoleculethatisformedbyusingtheDNAmoleculeasa templateandassemblingacomplementarysetofbases(althoughitcontains UracilinsteadofThymine).ThisRNAtravelsthroughthenuclearporestothe ribosomewhereproteinsareformedbasedonthesequencethatwas transcribedinthenucleus. mutation ApermanentchangeinthesequenceofbasesintheDNA;eithergerm-lineor somatic polypeptide chain Achainofaminoacidsthatarejoinedtooneanotherbyapeptidebond ribosomes ResponsibleforthesynthesisofproteinsusingmRNAasatemplate;composed oftwosubunits termination Thirdandfinalstepofproteinsynthesis,inwhichthepolypeptideandthe assembledcomponentsthatcarriedoutproteinsynthesisareseparatedfrom oneanother transcription Thefirststageofgeneexpression;processinwhichaportionofDNAservesasa templateformRNAformation transfer RNA (tRNA) Anucleicacidcontainingthesugarribosethatisresponsibleforbringingthe appropriateaminoacidtotheribosomeforproteinformation translation Duringgeneexpression,theprocessinwhichthesequenceofmRNAbases determinesthesequenceofaminoacidsinapolypeptide