* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Classical and genetic approaches to vertebrate development using
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Chemical biology wikipedia , lookup
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
History of biology wikipedia , lookup
Expression vector wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Neurogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Cell (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Symbiogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to genetics wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in stem-cell differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
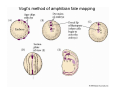
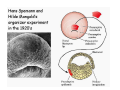
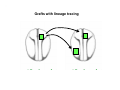
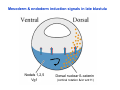
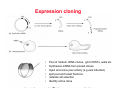
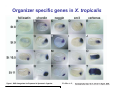
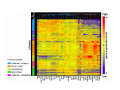
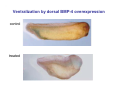
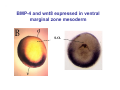
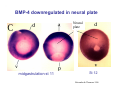
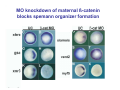
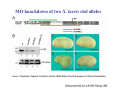
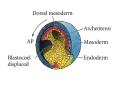
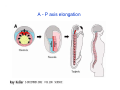
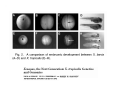
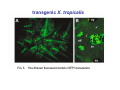
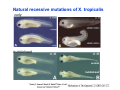
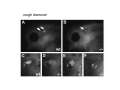
Classical and genetic approaches to vertebrate development using amphibians Gerald Thomsen State University of New York–Stony Brook [email protected] Amphibian Model Xenopus laevis QuickTime™ and a Photo - JPEG decompressor are needed to see this picture. Studying Development with Amphibian Embryos 1. Classical Approaches - “cut and paste” 2. Induction and cell differentiation assays 3. Functional screens for developmental regulators 4. Analysis of candidates by gain and loss of function 5. Cell biology and morphogenesis 6. Gene regulation 7. Genetics - Xenopus tropicalis and the future… 1. Classical Approaches • • • • Fate maps Explants - specification Transplants - induction Physical/chemical perturbation Vogt’s method of amphibian fate mapping Making a fate map of Xenopus Fluorescent dextran labeling of Building the frog 32 cell stage fate map: C1 C4 Dale and Slack 1984 Fate map of the Xenopus blastula Classical approaches: • Specification test – Autonomous execution of a developmental program. – Test cell’s or tissue’s potential for autonomous differentiation when removed from the embryo. – Gives clues about the nature of cell fate determination: determinants or induction? Specification test on Xenopus blastula epidermis Specification tests led to screens that identified localized RNAs - some are cell fate determinants . Animal pole: An-1 RNA helicase An-2 Mitochondrial ATPase subunit An-3 Zinc finger protein Smurf1 Ubiquitin ligase = neurectoderm Ectodermin Ubiquitin ligase = neurectoderm Vegetal pole Vg1 Xlsrts Wnt-11 VegT TGFß member = mesendoderm Structural RNA anchors Vg1 Wnt growth factor – dorsal axis, PCP T-box txn factor = mesendoderm • dozens isolated, mostly by differential cDNA screening • localization mechanisms somewhat understood. Tissue transplantation to test cell commitment – Do cells respond to their neighbors or are they committed to their own progranms? – Induction is where interactions between cells affects fate. – First evidence that vertebrates use induction to develop was demonstrated with amphibians (newts) Pieter Nieuwkoop showed that mesoderm is induced Grafts with lineage tracing 1. Classical Approaches - “cut and paste” 2. Induction and cell differentiation assays 3. Functional screens for developmental regulators 4. Analysis of candidates by gain and loss of function 5. Cell biology and morphogenesis 6. Gene regulation 7. Genetics - Xenopus tropicalis and the future… Animal cap assay to screen for inducers = test substance e.g. growth factor Animal cap assay to screen for inducers * = test substance e.g. growth factor * A popular variation is to inject a candidate mRNA into the animal pole and test its effects on the isolated cap Mesenchyme & blood induction by BMP-4 Untreated Treated with BMP Mesenchyme, blood untreated + Vg1 nodals and activin act similarl Mesoderm & endoderm induction signals in late blastula Nodals 1,2,5 Vg1 Dorsal nuclear ß-catenin (cortical rotation &/or wnt11) 1. Classical Approaches - “cut and paste” 2. Induction and cell differentiation assays 3. Functional screens for developmental regulators 4. Analysis of candidates by gain and loss of function 5. Cell biology and morphogenesis 6. Gene regulation 7. Genetics - Xenopus tropicalis and the future… Expression cloning • • • • • • Pool of random cDNA clones, grid of ESTs, wells etc Synthesize mRNA from pooled clones Inject and score pool activity (e.g axis induction) split pool and retest fractions reiterate sib selection Identify active clone Chordin gene expression in Spemann Organizer head mesoderm notochord initial gastrulation (stage 10) Sasai et al, Cell. 1996 early gastrulation (stage 10.5) end of gastrulation (stage 13) Noggin gene expression in Spemann Organizer and notochord Stage 10 Smith & Harland (1996) Stage 10 Stage 13 Stage 13 Some key developmental genes isolated by expression cloning in Xenopus • • • • • • Noggin Chordin Sizzled Cerberus Dickkopf Kremen Organizer specific genes in X. tropicalis Kokha et al, Other ways to find candidates…. •Differential screen – subtractive selection – gene chip assay - e.g. VegT induced genes. – in silico = NCBI Differential Display (DD) • Protein interaction partners - Y2H, proteomics • Systems biology Networks • MFCG (my favorite cool gene…) 1. Classical Approaches - “cut and paste” 2. Induction and cell differentiation assays 3. Functional screens for developmental regulators 4. Analysis of candidates by gain and loss of function 5. Cell biology and morphogenesis 6. Gene regulation 7. Genetics - Xenopus tropicalis and the future… Does my favorite gene have a developmental function? • Gain of function tests – Overexpress gene of interest in embryo and observe effects. Induction of an ectopic dorsal axis by a constitutively active Type I activin receptor (ALK4) Ventralization by dorsal BMP-4 overexpression control treated BMP-4 and wnt8 expressed in ventral marginal zone mesoderm S.O. BMP-4 downregulated in neural plate Neural plate midgastrulation st 11 St 12 Brivanlou & Thomsen 1996 • Loss of function tests – Dominant-negative proteins – Antisense oligonucleotide targeting of mRNAs to block protein expression. • RNAse-H mediated destruction via DNA oligo • Translation inhibition with Morpholino oligo • Splicing inhibition with Morpholino – Gene mutations? DNA oligo-mediated mRNA destruction by endogenous oocyte RNAseH Slack 2000 RNAseH-mediated depletion of materna ß-catenin mRNA by antisense DNA oligos ß-catenin depleted embryos Rescue with injected ß-catenin mRNA MO knockdown of maternal ß-catenin blocks spemann organizer formation MO knockdown of two X. laevis chd alleles Region-specific D-V patterning gene expression 1. Classical Approaches - “cut and paste” 2. Induction and cell differentiation assays 3. Functional screens for developmental regulators 4. Analysis of candidates by gain and loss of function 5. Cell biology and morphogenesis 6. Gene regulation 7. Genetics - Xenopus tropicalis and the future… Cell biological observations and perturbations • cell shape and cytoarchitecture • cytoskeleton and nuclear structure / assembly • adhesion • movement • cell and tissue polarity A - P axis elongation 1. Classical Approaches - “cut and paste” 2. Induction and cell differentiation assays 3. Functional screens for developmental regulators 4. Analysis of candidates by gain and loss of function 5. Cell biology and morphogenesis 6. Gene regulation 7. Genetics - Xenopus tropicalis and the future… Gene regulation • promoter analysis - mutate and inject into nucleus • transgenics- stable, heritable, link tissue-specific promoters to reporters (GFP, RFP, etc)…basis of screens? • Transcription factor assays/purification with egg/embryo extracts- “get in the cold room”…or modern proteomics • inducible systems – Stage specific promoters – Heat shock promoter – Protein chimeras - fused regulatory domains (e.g. GR) Also …purification of regulatory proteins - & use of egg and embryo in vitro extracts • • • • • • Cell cycle regulators…e.g MPF = cyclin + cdk Transcription factors Replication factors Translation systems Protein degradation / ubiquitin-proteasome Chromatin assembly 1. Classical Approaches - “cut and paste” 2. Induction and cell differentiation assays 3. Functional screens for developmental regulators 4. Analysis of candidates by gain and loss of function 5. Cell biology and morphogenesis 6. Gene regulation 7. Genetics - Xenopus tropicalis and the future… Enter Xenopus tropicalis X.l X.t. transgenic X. tropicalis Cardiac actin- RFP Pax6-GFP Lens gamma crystalline- RFP + Pax6-GFP = yellow eye Natural recessive mutations of X. tropicalis curly bubblehead Mutants recovered from a gynogentic haploid screen rough diamond balloon head Fly First mutant: Morgan 1910 Genome: ~ 2001 Xenopus Harland, Grainger 2005 2005 The starlet sea anemone, Nematostella vectensis (Anthozoa) egg masses Lab of Mark Q. Martindale Deuterostomia Bryozoa Articulata Phoronida-* Inarticulata Pr otostomia Spiralia Acoelomorpha-* Cnidaria-* Ctenophora-* Porifera Choanoflagellata “Bilateria” “Radiata” Metazoa