* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lesson Overview Evolution and Ecology
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Group selection wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
The Selfish Gene wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
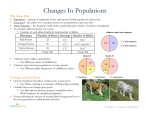
8/5/2011 Lesson Overview Natural Selection Evolution Adaptations Ad t ti 1 Evolution and Ecology To understand animal distributions and habitat use, we must understand the framework upon which these relationships are built. - Definitions - Management Implications 2 Gene Small unit of a DNA molecule arranged in linear order along microscopic threadlike bodies or chromosomes. Coded for a specific protein to produce one of the many attributes of a species. Unit material of inheritance 3 1 8/5/2011 Allele Alternate forms of a gene. - Dominant allele masks the expression of another. - Recessive allele is masked byy dominant allele. In most multicellular organisms each individual cell contains two copies of each type of chromosome (alleles of gene). - One inherited from ovum and one from sperm. 4 Genotype Pair of alleles. Two types of Genotypes - Heterozygous yg • Two copies of gene are different. - Homozygous • Two copies of gene are the same. 5 Phenotype The outward appearance of an organism for a given characteristic. The observable expression of the genotype. 6 2 8/5/2011 Natural Selection Differential success of individuals within the population that results from their interaction with the environment. - Reproduction and survival of different genotypes. - The result of natural selection is evolution. 7 Evolution Progressive changes in the frequency and types of genes in populations due to natural selection. - Theory explaining changes in individuals of a species i over titime. - Evolution occurs over generations. Major Sources - Mutation - Genetic recombination - Gene flow 8 Survival To live long enough to successfully reproduce offspring which in turn can live and successfully reproduce. 9 3 8/5/2011 Fitness An individual’s fitness is measured by the proportion of its genes left in the gene pool. - Long-term reproductive success. 10 Adaptation A genetically determined characteristic that improves an organism’s ability to survive, grow and reproduce under the prevailing environmental conditions. - Behavioral - Morphological - Physiological 11 Biological Rules Allen's Rule - Animal extremities are shorter in colder parts of its range than in warmer parts. Bergman's Rule - Geographic G hi races off species i with ith smaller ll b body d size i are found in warmer parts and larger body size in colder parts of the species range. Gloger's Rule - Dark pigments increase in warm and humid habitats. 12 4 8/5/2011 Why species here? Factors responsible for presence of animals in an area are complicated, interactive, and usually not readily apparent. Current animal distributions are the result of natural selection (their path through the complex interactions of selective pressures over time). Understanding life histories improves efforts in habitat management. 13 Why species here? To understand why a population is found in a specific area requires knowledge of the organism’s ecological relationships: - Soil, temperature, and biotic regimes - Biogeographic history - Effects of competition and predation which may affect behavior and habitat use. 14 End of Lesson Natural Selection Evolution Adaptations p 15 5