* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download SynCAM2a ΔPDZ Δ4.1B ΔPDZ - University of Oregon (SPUR)
Histone acetylation and deacetylation wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Secreted frizzled-related protein 1 wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
P-type ATPase wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Protein adsorption wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
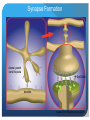
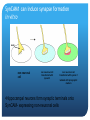
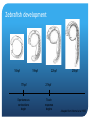
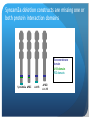
The role of of SynCAM2a in synapse formation Sofia Nakhnikian-Weintraub, Smith College 2012 Mentor: Courtney Easley-Neal, PI: Phil Washbourne Synapse Formation Axonal growth cone filopodia SynCAMs dendrite Adapted from Washbourne et al 2004 SynCAM1 can induce synapse formation in vitro axon non neuronal cell non neuronal cell transfected with syncam1 non neuronal cell transfected with syncam1 labeled with presynaptic markers •Hippocampal neurons form synaptic terminals onto SynCAM- expressing non-neuronal cells SynCAM structure •SynCAMs are present in mice, zebrafish and humans •All contain 3 immunoglobulin (IG) domains, a transmembrane domain, and a 4.1 binding and PDZ binding domain Experimental Plan Subclone 4 SynCAM2a constructs (full-length, and 3 deletions: 4.1B, PDZ, and 2X [both protein binding domains] deletions into a vector with a fluorescent tag. Microinject zebrafish embryos with the 4 constructs. Stain known pre and postsynaptic proteins through immunohistochemistry (IHC) to determine whether SynCAM is present at synapses in the zf spinal cord, and to assess whether colocalization occurs between synaptic proteins and SynCAM Why use Zebrafish? Zebrafish, like humans, are vertebrates. Zebrafish develop rapidly, and have functional nervous systems within 1 day. The embryos are fertilized externally and there is no parental care, allowing for collection and manipulation of eggs. Zebrafish are transparent for the first few days of life, allowing in vivo experimentation, and live imaging. Zebrafish development 16hpf 19hpf 17hpf Spontaneous contractions begin 22hpf 25hpf 21hpf Touch response begins Adapted from Kimmel et al 1995 SynCAM2a expression in RB cells involved in the touch response Touch response circuitry In situ 24 hpf SynCAM2a expression Restricting expression of SynCAM2a with transgenic lines • We have a line that expresses gal4 in the RBs, I will inject with a UAS SynCAM2a full length and dominant negative construct. Syncam2a deletion constructs are missing one or both protein interaction domains Transmembrane domain 4.1B domain PDZ domain SynCAM2a ΔPDZ Δ4.1B ΔPDZ/ Δ 4.1B Steps for making S2a fl and deletion constructs Insert: PCR, TOPO cloning, miniprepping, restriction digest Vector: Digest, dephosphoryolation Insert Vector backbone Ligation, transformation Miniprepping – isolating the DNA from bacteria. Complete plasmid Microinjection is a method used to introduce DNA constructs into embryos A capillary needle is used to inject 3-4 nL of the DNA constructs into one cell embryos. New cloning strategy The fluorescent tag was inhibiting protein function, so we will attach the tag to the other end of the protein. Subclone in pieces: signal sequence, coding sequence and fluorescent tag Instead of UAS S2a full length-make we will make UASsignal sequence-mkate-S2a (coding sequence)-full length This adds several steps to the cloning process Antibody staining (IHC) of pre and post synaptic proteins Future Directions Finish cloning the new constructs Inject embryos with the constructs Confirm presence of SynCAM2a at synapses with full length construct Assess affect of the dominant negative constructs on protein recruitment and synaptic function Behavioral analysis of fish expressing full-length and dominant negative constructs