* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download RNA and Protein Synthesis
Promoter (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Protein (nutrient) wikipedia , lookup
Protein adsorption wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Bottromycin wikipedia , lookup
RNA interference wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Eukaryotic transcription wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
RNA polymerase II holoenzyme wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
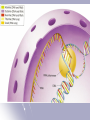
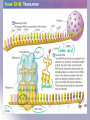
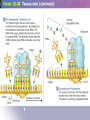
RNA and Protein Synthesis 12.3 p.336-341 RNA RNA = ribonucleic acid RNA has many jobs, but its main job is protein synthesis. Structure RNA Ribose sugar Single-stranded Uracil replaces thymine to pair with adenine DNA Deoxyribose sugar Double-stranded Thymine pairs with adenine 3 Types of RNA 1.Messenger RNA (mRNA)—carries information from the nucleus to the ribosome. A 3 base sequence is called a codon. It codes for the 20 amino acids. 2. Ribosomal RNA (rRNA)—contained in the ribosome where proteins are made. It reads the mRNA and sends a chemical message to the tRNA to bring the anticodon. 3.Transfer RNA (tRNA)—transfers each amino acid and anticodon to the appropriate place on the mRNA strand. Transcription=part of the nucleotide sequence of DNA is copied into a complementary sequence of RNA. 1. The enzyme RNA polymerase binds to and unzips the DNA. It uses 1 strand as a template. 2. A single strand of mRNA is made. (U) replaces (T). 3. mRNA breaks off from the DNA, leaves the nucleus and goes to the ribosome. 4. DNA zips back together. Codons These codons are used to form the polypeptide (protein) in the right order. AUG serves as a “start” codon. (or methionine) There are 3 “stop” codons that signal the end of the polypeptide. There are 64 possible three-base codons for mRNA (4x4x4=64) Genetic code Molecular Genetics Translation=the decoding of an mRNA into a polypeptide chain (protein) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. mRNA brings the codons to the ribosome. Start codon, AUG, is always first. tRNA brings an amino acid on one end and an anticodon on the other end. Anticodon pairs with the complementary codon. This continues until a stop codon is reached. Amino acid chain (protein) is released. Recap Transcription happens in the nucleus DNA to mRNA Translation happens in the cytoplasm (ribosome) mRNA to polypeptide (protein) mRNA has the codons tRNA has the anticodons and the amino acids Jokes are next!