* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download hydrophobic interaction chromatography.
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Immunoprecipitation wikipedia , lookup
Ancestral sequence reconstruction wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
Protein (nutrient) wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Theories of general anaesthetic action wikipedia , lookup
Model lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Protein domain wikipedia , lookup
Protein folding wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Size-exclusion chromatography wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Intrinsically disordered proteins wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Protein purification wikipedia , lookup
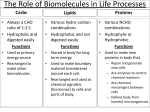
Hydrophobic Interaction Dr. Nikhat Siddiqi 1 • Soluble proteins require a solvation shell of water on their surface to maintain solubility in aqueous solution. • This water masks hydrophobic groups that also exist on the protein surface. In the presence of reagents that are capable of binding water from the solvation shell (e.g. (NH4)2SO4), it is possible to disrupt solvation and expose these hydrophobic groups. Dr. Nikhat Siddiqi 2 • Using a hydrophobic stationary phase such as provided by bonded octyl (strongly hydrophobic) or phenyl (more weakly hydrophobic) groups, it is possible to promote hydrophobic interactions between protein and such a bonded phase. This is the basis of the adsorption chromatography technique called hydrophobic interaction chromatography. Dr. Nikhat Siddiqi 3 • Protein samples are applied to columns containing octyl or phenyl groups in the presence of a large concentration (approx. 2 M) of a highly polar solvent such as (NH4)2SO4. • In such solvents, hydrophobic interactions are strongly promoted between proteins and the stationary phase. • Applying a decreasing gradient of solvent polarity, (e.g. 20M (NH4)2SO4) gradually disrupts hydrophobic interactions, thus separating proteins (with different net hydrophobicity) from each other. • Alternatively, elution may be achieved by the use of a hydrophobic displacer molecule such as a nonionic detergent (e.g. Triton X-100), an aliphatic amine (e.g. butylamine) or an aliphatic alcohol (e.g. butanol). Dr. Nikhat Siddiqi 4 • Since (NH4)2SO4 precipitation is frequently an early stage in protein purification, this type of chromatography may be conveniently used subsequent to this step in a protein purification strategy. • Important experimental variations in this technique include; using stationary phases of differing hydrophobicities (e.g. phenyl or octyl), different buffer concentrations and composition, varying pH (lower pH favours binding) and temperature (higher temperature favours binding). Dr. Nikhat Siddiqi 5 Dr. Nikhat Siddiqi 6