* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download How Prejudiced Are People?
Survey
Document related concepts
Social loafing wikipedia , lookup
Memory conformity wikipedia , lookup
Belongingness wikipedia , lookup
James M. Honeycutt wikipedia , lookup
In-group favoritism wikipedia , lookup
Attitude (psychology) wikipedia , lookup
Social dilemma wikipedia , lookup
Group polarization wikipedia , lookup
Relational aggression wikipedia , lookup
Attitude change wikipedia , lookup
Albert Bandura wikipedia , lookup
Self-categorization theory wikipedia , lookup
Social tuning wikipedia , lookup
Group dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Communication in small groups wikipedia , lookup
False consensus effect wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
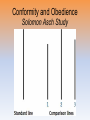
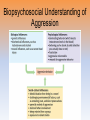
superior racist prejudiced assertive rude grumpy possessive germophobe fearless “Lady seemed annoyed but she probably reacted that way because she was in a hurry.” “kindness of strangers…” “bad day” “mistake displayed characteristics of two individuals” “assumptions because of race” “affect her prejudice?” http://www.youtube.com/watc h?v=epuTZigxUY8 The Lunch Date 10:00 Unit 14: Social Psychology Unit Overview • Social Thinking – Objectives 1&2 • Social Influence – Objectives 3-7 • Social Relations – Objectives 8-17 Click on the any of the above hyperlinks to go to that section in the presentation. Introduction • Social Psychology – the scientific study of how we think about, influence, & relate to one another. Social Thinking Attributing Behavior to Persons or to Situations • Attribution theory – We credit a person’s behavior with either their traits (disposition or the situation/environment) – Dispositional vs. situational attribution –Fundamental attribution error – tendency for observers, when analyzing another’s behavior, to underestimate the impact of the situation and to overestimate the impact of personality traits – Self-serving bias Attributing Behavior to Persons or to Situations The Effects of Attribution • Personal relationships –happy vs. unhappy couples • Politics –poverty & unemployment • conservatives / liberals • Job Relationships Our attributions to individuals dispositions or to their situations should be made carefully as they have real consequences. http://www.youtube.com/watc h?v=epuTZigxUY8 The Lunch Date 10:00 Objective 2: Attitudes and Actions • Attitude – feelings that predispose us to act – Central route persuasion – Peripheral route persuasion – social pressures can weaken the attitudebehavior connection Actions Affect Attitudes • The Foot-in-the-Door Phenomenon –you can come to believe an idea you support… –inducing people to act against their beliefs can affect their attitude – “start small and build” – racial attitudes - moral action strengthens moral conviction easier to change attitudes than actions = Attitudes are internal – Actions are observed by all. People assume we act according to our attitudes, so if an action conflicts we change attitude to fit action. Actions Affect Attitudes • Cognitive Dissonance: Relief From Tension –Cognitive dissonance theory –“Attitudes follow behavior” – the theory that we act to reduce the discomfort (dissonance) we feel when two of our thoughts (cognitions) are inconsistent. For example, when our awareness of our attitudes and of our actions clash, we can reduce the resulting dissonance by changing our attitudes. Actions Affect Attitudes • Role-Playing Affects Attitudes –Role –Stanford Prison Study (Philip Zimbardo) –Abu Ghraib Stanford Prison Experiment http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=sZwfNs1pqG0 13 minutes Social Influence Written… 1. X = 36.23 Sx = 15.4 Verbal… 1. X = 30.38 Sx = 14 3. X= 34.67 Sx = 14.5 3. X = 37 Sx = 10.45 5. X = 43 Sx = 12.30 5. X = 48 Sx = 14 Conformity and Obedience • Chameleon effect –Unconsciously mimicking others • Yawning • Looking up when others do • Mood linkage –Sharing up & down moods Conformity & Obedience Group Pressure and Conformity • Conformity – Adjusting behavior\thinking toward group standard – Solomon Asch study – http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=NyDDyT1lDhA Conformity and Obedience Solomon Asch Study Conformity and Obedience Group Pressure and Conformity • Conditions That Strengthen Conformity – One is made to feel incompetent or insecure – Group has at least three people – Group is unanimous – One admires the group’s status – One has made no prior commitment – Others in group observe one’s behavior – One’s culture strongly encourages respect for social standards Conformity and Obedience Group Pressure and Conformity Normative social influence Reasons for Conforming: • desire to gain approval or avoid disapproval. (to be seen as normal) Informational social influence • willingness to accept other’s opinions about reality When accuracy of judgment is important, but easy = rarely conform. When important but difficult = conform ½ the time Obedience • Stanley Milgram http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3f6LL V3fkXg (14 min) Conformity and Obedience Obedience Conformity and Obedience Obedience Conformity and Obedience Obedience Follow up studies –authority figure close at hand –prestigious university –victim depersonalized –no role models of defiance Conformity and Obedience Obedience Conformity and Obedience Lessons From the Conformity and Obedience Studies • Ordinary people being corrupted by an evil situation • foot-in-the-door • 93% complied when others did the shocking • attributing responses to evil disposition misses the point – people OBEY, not evil – teacher select level of shock • only 1 went to 450 v • 45-60 v Group Influence Individual Behavior in the Presence of Others • Social Facilitation – stronger responses on simple or well-learned tasks in the presence of others –Task difficulty –Expertise effects • what you do well, you’re likely to do better in front of an audience – Crowding effects • reactions are amplified Group Influence What happens to performance when people perform a task as a group? • Social Loafing –exert less effort when common goal • men • individualistic cultures –Reasons why? • Less accountability • contribution is dispensable Group Influence Individual Behavior in the Presence of Others • Deindividuation – the loss of self-awareness and self-restraint occurring in group situations that foster arousal and anonymity. Group Influence Effects of Group Interaction • Group Polarization – the enhancement of a group’s prevailing inclinations through discussion with the groups Group Influence Effects of Group Interaction • Group Polarization – the enhancement of a group’s prevailing inclinations through discussion with the groups Group Influence Effects of Group Interaction • Group Polarization – the enhancement of a group’s prevailing inclinations through discussion with the groups Group Influence Effects of Group Interaction • Group Polarization – the enhancement of a group’s prevailing inclinations through discussion with the groups Group Influence Effects of Group Interaction • Group Polarization – the enhancement of a group’s prevailing inclinations through discussion with the groups Group Influence Effects of Group Interaction • Group Polarization – the enhancement of a group’s prevailing inclinations through discussion with the groups Group Influence Effects of Group Interaction • Groupthink – mode of thinking that occurs when the desire for harmony in a decision-making group overrides a realistic appraisal of alternatives –Bay of Pigs –Challenger explosion Cultural Influence • Culture –Culture within animals –Culture in humans Cultural Influence Variations Across Cultures • Norm = prescribe proper behavior –Personal space –Pace of life Cultural Influence Variation Over Time • Changes over the generations The Power of Individuals (Objective #8 / FITB #24-26) • Social control vs personal control • Minority influence Social Relations Prejudice How Prejudiced Are People? • Prejudice • Stereotype • Discrimination Prejudice How Prejudiced Are People? Prejudice How Prejudiced Are People? Prejudice How Prejudiced Are People? Prejudice How Prejudiced Are People? Prejudice How Prejudiced Are People? Prejudice How Prejudiced Are People? • • • • • Unconscious racial associations Unconscious patronization Race-influenced perceptions Other-race effect Reflexive body responses – Facial muscles / amygdala Prejudice Social Roots of Prejudice • Social Inequalities – blame the victim • victim: anger or self-blame • Us and Them: Ingroup and Outgroup – Ingroup (Ingroup bias) – Outgroup • most intense dislike • Emotional roots of prejudice – Scapegoat theory Emotional Roots of Prejudice –Scapegoat theory • target for one’s anger • “fear & anger create aggression, aggression against citizens of another race or ethnicity creates racism.” Prejudice Cognitive Roots of Prejudice • Categorization – Outgroup homogeneity • overestimate the similarity of those in others groups – Other-race effect • Vivid cases – overgeneralizing • Just-world phenomenon – Hindsight bias Aggression • Aggression – reactively – proactively Aggression The Biology of Aggression • Genetic Influences • Neural Influences –neural system that needs to be provoked (frontal lobe inhibits) • Biochemical Influences –hormones (testosterone), alcohol, Aggression Psychological and Social-Cultural Factors in Aggression • Aversive Events –Frustration-aggression principle • Social and cultural influences –Aggression-replacement program Aggression Psychological and Social-Cultural Factors in Aggression • Observing models of aggression –Rape myth • Acquiring social scripts • Do video games teach, or release violence? –Catharsis hypothesis? Biopsychosocial Understanding of Aggression Biopsychosocial Understanding of Aggression Biopsychosocial Understanding of Aggression Biopsychosocial Understanding of Aggression Attraction The Psychology of Attraction • Proximity –Mere exposure effect • Physical attractiveness • Similarity –Reward theory of attraction Attraction Romantic Love • Love –Passionate love –Companionate love • Equity • Self-disclosure Altruism • Altruism –Kitty Genovese • Bystander Intervention –Diffusion of responsibility –Bystander effect Altruism Altruism Altruism Altruism Altruism Altruism Altruism Altruism Altruism Altruism The Norms of Helping • Social exchange theory • Reciprocity norm • Social-responsibility norm Conflict and Peacemaking • Conflict • Social trap –Non-zero sum game Conflict and Peacemaking Enemy Perceptions • Mirror-image perceptions • Self-fulfilling prophecy Conflict and Peacemaking • Contact • Cooperation –Superordinate goals • Communication • Conciliation –GRIT The End • Types of Files Teacher Information – This presentation has been saved as a “basic” Powerpoint file. While this file format placed a few limitations on the presentation, it insured the file would be compatible with the many versions of Powerpoint teachers use. To add functionality to the presentation, teachers may want to save the file for their specific version of Powerpoint. • Animation – Once again, to insure compatibility with all versions of Powerpoint, none of the slides are animated. To increase student interest, it is suggested teachers animate the slides wherever possible. • Adding slides to this presentation – Teachers are encouraged to adapt this presentation to their personal teaching style. To help keep a sense of continuity, blank slides which can be copied and pasted to a specific location in the presentation follow this “Teacher Information” section. Definition Slides Social Psychology = the scientific study of how we think about, influence, and relate to one another. Attribution Theory = the theory that we explain someone’s behavior by crediting either the situation or the person’s disposition. Fundamental Attribution Error = the tendency for observers, when analyzing another’s behavior, to underestimate the impact of the situation and to overestimate the impact of personal disposition. Attitude = feelings, often influenced by our beliefs, that predispose us to respond in a particular way to objects, people, and events. Central Route Persuasion = attitude change path in which interest people focus in which interested people focus on the arguments and respond with favorable thoughts. Peripheral Route Persuasion = attitude change path in which people are influenced by incidental cues, such as a speaker’s attractiveness. Foot-in-the-Door Phenomenon = the tendency for people who have first agreed to a small request to comply later with a larger request. Role = a set of expectations (norms) about a social position, defining how those in the position ought to behave. Cognitive Dissonance Theory = the theory that we act to reduce the discomfort (dissonance) we feel when two of our thoughts (cognitions) are inconsistent. For example, when our awareness of our attitudes and of our actions clash, we can reduce the resulting dissonance by changing our attitudes. Conformity = adjusting one’s behavior or thinking to coincide with a group standard. Normative Social Influence = influence resulting from a person’s desire to gain approval or avoid disapproval. Informational Social Influence = influence resulting from one’s willingness to accept other’s opinions about reality. Social Facilitation = stronger responses on simple or welllearned tasks in the presence of others. Social Loafing = the tendency for people in a group to exert less effort when pooling their efforts toward attaining a common goal than when individually accountable. Deindividuation = the loss of self-awareness and selfrestraint occurring in group situations that foster arousal and anonymity. Group Polarization = the enhancement of a group’s prevailing inclinations through discussion with the groups. Groupthink = the mode of thinking that occurs when the desire for harmony in a decision-making group overrides a realistic appraisal of alternatives. Culture = the enduring behaviors, ideas, attitudes, values, and traditions shared by a group of people and transmitted from one generation to the next. Norm = an understood rule for accepted and expected behavior. Norms prescribe “proper” behavior. Personal Space = the buffer zone we like to maintain around our bodies. Three Causes of Prejudice • Social – In Group vs. Out Group • Cognitive – Just World – Categorize – Vivid Cases • Emotional – Scapegoat Theory Prejudice = an unjustifiable (and usually negative) attitude toward a group and its members. Prejudice generally involves stereotyped beliefs, negative feelings, and a predisposition to discriminatory action. Stereotype = a generalized (sometimes accurate but often overgeneralized) belief about a group of people. Discrimination = unjustifiable negative behavior toward a group and its members. Ingroup = “Us” – people with whom we share a common identity. Outgroup = “Them” – those perceived as different or apart from our ingroup. Ingroup Bias = the tendency to favor our own group. Scapegoat Theory = the theory that prejudice offers an outlet for anger by providing someone to blame. Other-race Effect = the tendency to recall faces of one’s own race more accurately than faces of other races. Also called the cross-race effect and the own-race bias. Just-World Phenomenon = the tendency for people to believe the world is just and that people therefore get what they deserve and deserve what they get. Causes of Aggression • Genetic • Neural • Biochemical • • • • • Psychological & Social Aspects of Aggression Frustration – Aggression Principle Aggression Replacement Models Social Scripts Catharsis Hypothesis Aggression = any physical or verbal behavior intended to hurt or destroy. Frustration-aggression Principle = the principle that frustration – the blocking of an attempt to achieve some goal – creates anger, which can generate aggression. Mere Exposure Effect = the phenomenon the repeated exposure to novel stimuli increases liking of them. Passionate Love = an aroused state of intense positive absorption in another, usually present at the beginning of a love relationship. Companionate Love = the deep affectionate attachment we feel for those with whom our lives are intertwined. Equity = a condition in which people receive from a relationship in proportion to what they give to it. Self-Disclosure = revealing intimate aspects of oneself to others. Altruism = unselfish regard for the welfare of others. Bystander Effect = the tendency for any given bystander to be less likely to give aid if other bystanders are present. Social Exchange Theory = the theory that our social behavior is an exchange process, the aim of which is to maximize benefits and minimize costs. Reciprocity Norm = an expectation that people will help, not hurt those who have helped them. Social-Responsibility Norm = an expectation that people will help those dependent upon them. Conflict = a perceived incompatibility of actions, goals, or ideas. Social Trap = a situation in which the conflicting parties, by each rationally pursuing their selfinterest, become caught in mutually destructive behavior. Mirror-Image Perceptions = mutual views often held by conflicting people, as when each side sees itself as ethical and peaceful and views the other side as evil and aggressive. Self-Fulfilling Prophecy = a belief that leads to its own fulfillment. Superordinate Goals = shared goals that override differences among people and require their cooperation. GRIT = Graduated and Reciprocated Initiatives in Tension-Reduction – a strategy designed to decrease international tensions. Social Psychology FRQ