* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nouns • Noun phrase - builds around a simple noun (person, place
Udmurt grammar wikipedia , lookup
Compound (linguistics) wikipedia , lookup
Lithuanian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Arabic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ojibwe grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ukrainian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Old Irish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Old Norse morphology wikipedia , lookup
Macedonian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Lexical semantics wikipedia , lookup
Malay grammar wikipedia , lookup
Modern Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Zulu grammar wikipedia , lookup
Navajo grammar wikipedia , lookup
English clause syntax wikipedia , lookup
Georgian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Kannada grammar wikipedia , lookup
Portuguese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Swedish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Old English grammar wikipedia , lookup
Japanese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Esperanto grammar wikipedia , lookup
Chinese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Scottish Gaelic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Russian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Modern Hebrew grammar wikipedia , lookup
Icelandic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Italian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Romanian grammar wikipedia , lookup
French grammar wikipedia , lookup
Vietnamese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Latin syntax wikipedia , lookup
Yiddish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Serbo-Croatian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Polish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Spanish grammar wikipedia , lookup
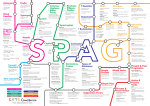
Nouns Noun phrase - builds around a simple noun (person, place, object) e.g. The dog - The old dog Expanded noun phrase - adjectives placed together in a sentence to describe the noun e.g. The old scruffy dog *Any phrase including an adjective is also classes as an adjectival phrase Abstract noun - cannot be is a feeling e.g. love, happiness, anxiety, despair, excitement Proper noun - real name for the noun e.g. man - Tom, town - Newcastle Pronoun - Uses the first/third person e.g. he, she, we, they Relative pronoun - form clauses in sentences marked with commas e.g. ,who was ..., ,which is ..., ,that is ..., Collective nouns - names for groups of nouns e.g. cows herd, geese - gaggle, team, choir Compound nouns - made up of more than one word e.g.pickpocket, waterbottle Concrete nouns - nouns you can see or touch e.g. chair, tree Verbs Verb - describes an action that is taking place e.g. running, skipping, sitting Adverb - tells us how the action is performed e.g sits quietly Adverbial phrase - expands the verb tells us when e.g. I will go to the shop in a minute tells us where e.g. The children are playing in the garden tells us how something is done e.g. He sleeps like a baby Adverbials can go anywhere in a sentence, fronted adverbials start a sentence e.g. Tomorrow I will got o school. Modal verbs - paired with a verb, modal verbs include ‘small’ words such as: must, will, may, should, could, would, shall, might, can Imperative verbs - not to be called ‘bossy’ verbs! These verbs give orders in a sentence, usually paired with an exclamation, never question sentences e.g. Stop that now! Sentences Simple sentences - these are not to be termed as boring, look at it as one idea with one clause Clause - verb must be present Complex sentences - two parts: Main clause - makes sense on its own, needs a verb Subordinating clause - adds another action of extra information to the sentence Embedded clause - a group of words that includes a subject and a verb, that is within a main clause, usually marked by commas. Information related to the sentence topic is put into the middle of the sentence to give the reader more information and enhance the sentence Parenthesis - use of a , - or () to add extra information but with no verb added Phrases - stand alone, could be replaced by a single word Active - focuses on the subject doing something (action) Passive - focuses on the object Connectives/Conjunctions Conjunctions - (within a sentence) co-ordinating: and, but, or, nor Adverbial - (within a sentence) subordinate/complex sentences: although, as, when, while, before, after, because, if *For children still term the ‘adverbials’ as conjunctions, adverbials help us identify the level of skill used and applied in writing. Connectives (termed as openers previously) at the beginning of sentences, connect time or reason/order events: First/Next/After/However/On the other hand. Even though/Nevertheless Preposition - tells us where (location) of a person/place/object is e.g. under, behind, next to, in, over