* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ch.4 Cell Notes - Milan Area Schools
Survey
Document related concepts
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Mechanosensitive channels wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Theories of general anaesthetic action wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Model lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
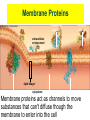
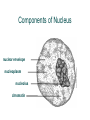
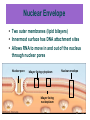
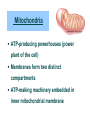
Cell Organelles and Features What do all of the parts do in a cell? Plasma (Cell) Membrane ● ● This surrounds the cell & controls what moves in and out of the cell like a gatekeeper Made of two layers of phospholipids (aka phospholipid bilayer) Phospholipid bilayer has polar heads that one layer point out & nonpolar of lipids tails that point in Figure 4.3 one layer of lipids Page 56 Membrane Proteins Recognition protein Receptor protein extracellular environment lipid bilayer cytoplasm Membrane proteins act as channels to move Protein pump Protein channel Protein pump across bilayer across bilayer substances that can't diffuse though the Figure 4.4 Page 57 membrane to enter into the cell Functions of Nucleus ● ● Keeps the DNA molecules of eukaryotic cells separated from the organelles in the cytoplasm Makes it easier to organize DNA and to copy it before parent cells divide into daughter cells Components of Nucleus nuclear envelope nucleoplasm nucleolus chromatin Nuclear Envelope ● Two outer membranes (lipid bilayers) ● Innermost surface has DNA attachment sites ● Allows RNA to move in and out of the nucleus through nuclear pores Nuclear pore bilayer facing cytoplasm Nuclear envelope bilayer facing nucleoplasm Figure 4.12b Page 63 Mitochondria ● ATP-producing powerhouses (power plant of the cell) ● Membranes form two distinct compartments ● ATP-making machinery embedded in inner mitochondrial membrane Mitochondrial Origins ● Mitochondria resemble bacteria – Divide on their own May have evolved from ancient bacteria that were engulfed but not digested – ● Have own DNA, ribosomes Endoplasmic Reticulum ● Aka “ER” - acts like a highway in the cell moving molecules from 1 part to another ● Extends throughout cytoplasm ● Two regions - rough (w/ ribosomes) – manufactures proteins - smooth (w/o ribosomes) – manufactures lipids Golgi Body ● ● ● ● Puts finishing touches on proteins and lipids that arrive from ER Packages finished material for shipment to final destinations (shipping department of the cell) Material arrives and leaves in vesicles budding vesicle