* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chemistry of Macromolecules
Survey
Document related concepts
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Theories of general anaesthetic action wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Mechanosensitive channels wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Ethanol-induced non-lamellar phases in phospholipids wikipedia , lookup
Lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Model lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
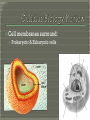
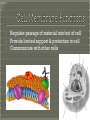
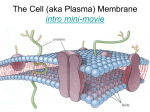
Biology Ch. 7-3 BIG biological molecules • Made of smaller parts Monomers Carbon-based (organic) • Carbohydrates • Nucleic acids • Proteins • Lipids Monomer? • Glycerol head • Fatty acid tail Used for: • Long term energy storage • Insulation • Major component of membranes • Signaling molecules and hormones Examples: • Fats, oils, waxes Found in: • All the good tasting foods Cell membranes surround: • Prokaryotic & Eukaryotic cells 1. 2. 3. Regulate passage of material into/out of cell Provide limited support & protection to cell Communicate with other cells Made of Phospholipids • phosphorus (hydrophilic) “head” • lipid (hydrophobic) “tail” Phospholipid bilayer • a double layer of phospholipids Protein Channels • allows large molecules to pass through Carbohydrate antennae • picks up messages from outside the cell Cholesterol • lipids that prevent freezing Carbohydrate antenna Phospholipid bilayer Protein channels The membrane is a fluid-mosaic: • Flexible; not rigid • Semi-permeable: picky about what enters/exits the cell Small Molecules move through bilayer • H2O, CO2 & O2 Large Molecules move through proteins • C6H12O6 (GLUCOSE) http://www.wiley.com/legacy/college/b oyer/0470003790/animations/membrane _transport/membrane_transport.htm http://www.susanahalpine.com/anim/Lif e/memb.htm