* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 15 Evolution
Sociocultural evolution wikipedia , lookup
Objections to evolution wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Unilineal evolution wikipedia , lookup
Organisms at high altitude wikipedia , lookup
Creation and evolution in public education in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and the Origin of Species wikipedia , lookup
Vestigiality wikipedia , lookup
Hindu views on evolution wikipedia , lookup
Punctuated equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Acceptance of evolution by religious groups wikipedia , lookup
Creation and evolution in public education wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
The eclipse of Darwinism wikipedia , lookup
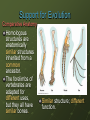
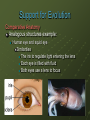
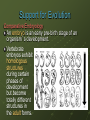
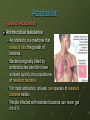
15.2 Evidence of Evolution Main idea: Multiple lines of evidence support the theory of evolution. Objectives: Describe how fossils provide evidence of evolution. Discuss morphological evidence of evolution. Explain how physiology and biochemistry provide evidence of evolution. New Vocabulary Derived trait Ancestral trait Homologous structure Vestigial structure Analogous structure Embryo Fitness Mimicry Camouflage Support for Evolution The theory of evolution states that all organisms on Earth have descended from a common ancestor. The fossil record offers some of the most significant evidence of evolutionary change. Fossils provide a record of species that lived long ago. Fossils show that ancient species share similarities with species that now live on Earth. Support for Evolution The Fossil Record The giant armadillo-like Glyptodon is an extinct animal that Darwin thought must be related to the living armadillos of today. The fossil record provides information for determining the ancestry of organisms and the patterns of evolution. Support for Evolution The Fossil Record Two major classes of traits: Derived traits are newly evolved features, such as feathers, that do not appear in the fossils of common ancestors. Ancestral traits are more primitive features, such as teeth and tails, that do appear in ancestral forms. Support for Evolution The Fossil Record Transitional fossils provide detailed patterns of evolutionary change for ancestors of many modern animals, including mollusks, horses, whales and humans. Example: Archeopteryx Shares features of both dinosaurs and birds. Support for Evolution Comparative Anatomy Homologous structures are anatomically similar structures inherited from a common ancestor. The forelimbs of vertebrates are adapted for different uses, but they all have similar bones. Similar structure; different function. Support for Evolution Comparative Anatomy Vestigial structures are the reduced forms of functional structures in other organisms. Evolutionary theory predicts that features of ancestors that no longer have a function for that species will become smaller over time until they are lost. Same structure; reduced function Examples: Snake pelvis, human appendix, blind fish and salamanders that live in caves but have eyes. Support for Evolution Comparative Anatomy Analogous structures can be used for the same purpose and can be similar in construction, but are not inherited from a common ancestor. Analogous structures show that functionally similar features can evolve independently in similar environments. Different structure; same function Support for Evolution Comparative Anatomy Analogous structures example: Human eye and squid eye Similarities The iris to regulate light entering the lens Each eye is filled with fluid Both eyes use a lens to focus function; Support for Evolution Comparative Embryology An embryo is an early pre-birth stage of an organism’s development. Vertebrate embryos exhibit homologous structures during certain phases of development but become totally different structures in the adult forms. Support for Evolution Comparative Biochemistry Common ancestry can be seen in the complex molecules that many different organisms share. Molecules are similar because the organisms have a common ancestor Species Sequence of Amino Acids in the same part of Hemoglobin Molecules Human Lys-Glu-His-Iso Horse Arg-Lys-His-Lys Gorilla Lys-Glu-His-Lys Chimpanzee Lys-Gu-His-Iso Zebra Arg-Lys-His-Arg The genomes of humans and chimpanzees differ by only about 1% of their genetic makeup Scientists now use similarities in DNA and RNA sequences to determine relationships between species Support for Evolution Geographic Distribution The distribution of plants and animals that Darwin saw during his travels first suggested evolution to Darwin. Rabbit in Europe Mara in S. America Support for Evolution Geographic Distribution Scientists have confirmed and expanded Darwin’s study of the distribution of plants and animals around the world in a field of study now called biogeography. Evolution is intimately linked with climate and geological forces. Adaptation An adaptation is a trait shaped by natural selection that increases an organism’s reproductive success. Fitness is a measure of the relative contribution an individual trait makes to the next generation. It is often measured as the number of reproductively viable offspring that an organism produces in the next generation. Adaptation Types of Adaptation Camouflage allows organisms to become almost invisible to predators. Some species have evolved morphological adaptations that allow them to blend in with their environments. Mimicry is another morphological adaptation that allows one species to evolve to resemble another species. Adaptation Types of Adaptation Can you see the peppered moth? Adaptation Types of Adaptation When disturbed, this octopus flashes and intensifies its stripes, resembling a poisonous sea snake. Unlike the sea snake, the octopus venom is harmless Adaptation Types of Adaptation Antimicrobial resistance An antibiotic is a medicine that slows or kills the growth of bacteria. Bacteria originally killed by antibiotics like penicillin have evolved quickly into populations of resistant bacteria. For most antibiotics, at least one species of resistant bacteria exists. People infected with resistant bacteria can never get rid of it. Adaptation Types of Adaptation Traits may decrease fitness Some features arise as a consequence of other evolutionary changes. • Human babies are born helpless at an earlier developmental stage than other primates as a consequence of the mother’s narrow birth canal. Narrow birth canal is an adaptation that enables walking on 2 legs instead of 4. Early birth is not an adaptation but instead a consequence of evolution.