* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 13 Review Adaptation: an inherited trait that helps an
Survey
Document related concepts
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
Transitional fossil wikipedia , lookup
Evolving digital ecological networks wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Theistic evolution wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Organisms at high altitude wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
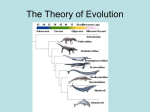
Chapter 13 Review Adaptation: an inherited trait that helps an organism survive Evolution: the process of how organisms acquire adaptations over time. (Change in a species over time) Diversity: a variety (5- 50 million living species) *scientists hypothesize that all life forms evolved from a common ancestor and new species branch off from earlier species (bacteria?) Cladogram (branching tree): a tree-like diagram that displays evolutionary relationships among living species and their ancestors Evidence of Evolution 1. Comparative anatomy (homologous structures, embryo development among vertebrates) 2. DNA 3. Fossils Comparative anatomy: the study of anatomical similarities and differences among species (arms, legs, head, hands, etc. Homologous structures: body structures that have a common origin bt do not necessarily perform the same function Vertebrates: animals with a backbone Fossils: remnant or trace of an organism from the past, such as a skeleton or leaf imprint, embedded and preserved in earth’s crust Finches led to Charles Darwin’s Theory of Evolution: beaks adapted for types of food they ate. They all had a common ancestor that they evolved from Natural selection: The process by which organisms with favorable adaptations survive and reproduce at a higher rate than organisms with less favorable adaptations. Artificial Selections: breeders select the desired traits to produce changes in a species over a few generations Darwin concluded that: 1. 2. 3. 4. Organisms change over time All organisms are descended from common ancestors by a process of branching Evolution is gradual, taking place over a long time The mechanism of evolution is natural selection Process of Natural Selection 1. Populations over-produce (weak die, strong survive and reproduce) 2. Individuals in population vary 3. Favorable adaptation are selected 4. Favorable adaptation accumulate Random mutations in genes produce variations of traits in a population Alleles: different forms of a gene (can cause mutations- helpful, harmful, or have no effect) Rr, RR, rr, RW, rw Mutations occur randomly in genes and produce variations Genetic variation: the variety of alleles in a population Genetic variation is necessary for natural selection and ensures that a population has a better chance of survival should the environment change NO VARIATION => NO EVOLUTION OCCURS MORE VARIATIONS => BETTER CHANCE OF SURVIVAL IF ENVIRONMENT CHANGES Isolation: occurs when populations become divided by an event (floods, volcanic, eruptions, mountain/canyon formation, earthquakes, new river forming) New species evolve due to: Isolation Adaptation Species formation (when isolated populations become so different that they can no longer interbreed) Extinction: occurs when the environment change and the adaptations of a species are no longer sufficient for its survival. (Main cause is loss of habitat caused by human destruction) Moth Population