* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download V: 0
Survey
Document related concepts
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
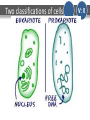
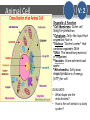
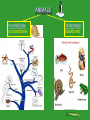
DO NOW V: 0 Monday Answer on page 60 of your INB… April 7, 2014 Organize these words in order from smallest to largest: •Atom •subatomic particle •Molecule •Cell •Ecosystem •Organelle •Tissue •organ system •Organism •Population •Organ DO NOW Monday Answer in your INB… April 7, 2014 ANSWER: V: 0 subatomic particle, atom, molecule, organelle, cell, tissue, organ, organ system, organism, population, ecosystem Homework & Agenda Homework Homework: STAAR Review Today’s Agenda -Parts of a cell -Cell Analogy -5 Kingdoms notes V: 0 TEKS V: 0 - Recognize levels of organization in plants and animals, including cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, and organisms -Differentiate between structure and function in plant and animal cell organelles, including cell membrane, cell wall, nucleus, cytoplasm, mitochondrion, chloroplast, and vacuole - Recognize that according to cell theory all organisms are composed of cells and cells carry on similar functions such as extracting energy from food to sustain life Vocabulary Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems Organisms Organelles Cell membrane V: 0 Cell wall Nucleus Cytoplasm Mitochondrion Chloroplast Vacuoles EQs & Objectives ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS: DAILY OBJECTIVES: Students will… -Identify the different parts of plant and animal cells V: 0 Cell Theory V: 0 1. All organisms (living things) are made of one or more cells. (Unicellular or multicellular) 2. The cell is the basic unit of all LIVING things. Hierarchy of all matter: Protons/ Neutrons/Electrons Atoms Elements Molecules Compounds Organelles Cells (LIFE) Tissues Organs Organ Systems Organisms Populations Ecosystems Earth Solar System Galaxy Local Group Galaxy Clusters Universe 3. All cells come from existing cells. (Mitosis=production of body cells or Meiosis=production of sex cells) Two classifications of cells O Prokaryotic Cells 1st form of life O Have NO nucleus – DNA is free (called the “nucleloid”) O ONLY form Unicellular organisms (one-celled) O Example: Bacteria (e. coli, staph, salmonella) O V: 0 O Eukaryotic Cells Evolved from prokaryotes O Have a nucleus with bundled DNA O Can form unicellular or multicellular organisms. O Example: Amoebas, plants animals, fungi, protists O *Note: There many TYPES of cells (skin, muscle, hair, sex, etc.,); these are the two categories that ALL cells fall under! It is the DNA within cells that controls what type of cell they will be. Two classifications of cells V: 0 Animal Cell V: 2 Organelle & Function *Cell Membrane: Outer cell lining for protection *Cytoplasm: Jelly-like liquid that organelles float in *Nucleus: “Control center” that contains organism’s DNA *DNA: The hereditary material of organisms *Vacuoles: Store nutrients and waste *Mitochondria: Jelly-bean shaped producers of energy (ATP) for cell EVALUATE: • What shape are the mitochondria? • How is the cell similar to a body system? Animal Cell V: 2 Plant Cell PLANT-SPECIFIC organelles: *Cell Wall: Gives plant cells shape and structure (rigidity), made of cellulose *Chloroplast: Site where photosynthesis in plant cells occurs EVALUATE: • What are some similarities between plant and animal cells? • What do you notice about the vacuole of the plant cell? • Why do you think plants evolved to have cell walls and animals did not? V: 2 Plant Cell V: 2 Cell Analogy V: 0 • Create an analogy of the cell to something you are familiar with, such as a store, mall, school, etc. • What does each part of the cell represent in your analogy? • Key Vocabulary: cell wall cell membrane vacuole chloroplast nucleus mitochondria cytoplasm Cell Analogy V: 0 Classification of Living Things Scientists estimate that there are between 3 million and 100 million species of organisms on Earth. Taxonomists--biologists who specialize in identifying and classifying life on our planet--have named approximately 1.7 million species so far. Each year, about 13,000 new species are added to the list of known organisms. So, how do scientists classify (organize) all these millions of species? The Big Picture 3 Domains and 6 Kingdoms Archaea The Archaea are one of two groups of prokaryotic organisms, organisms with no nuclear membrane. (Bacteria are the other group.) Archaea are believed to be the earliest form of life on Earth. Although both archaea and bacteria are simple life-forms, archaea are very different from bacteria. ARCHAEA Archaea do not require sunlight for photosynthesis, as plants do, and they do not need oxygen. Archaea absorb CO2, N2, or H2S and give off methane gas as a waste product. Archaea are best known for living in extremely hostile environments (very hot, very acid, or very salty), but they can also be found in less extreme conditions. Halococcus salifodinae is found in water with high concentrations of salt. Sulfolobus is an extrophile that lives in hot springs and thrives in sulfur-rich conditions. A Deep Sea Hydrothermal Vent – Prime Habitat for Archaea Extremophiles video of black smoker Hot springs in Yellowstone Park–“Hot” Spots for Archaean Extremophiles Prismatic Pool, Yellowstone Park Searching for Archaea in Yellowstone’s Obsidian Pool Archaea in Yellowstone Bacteria – the Most Abundant Organisms Bacteria (Staphylococcus aureus; yellow spheres) adhering to nasal cilia. E. Coli bacteria Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae Borrelia burgdorferi, the bacterium that causes Lyme disease. There are more bacteria in your mouth than there have been people living since the dawn of humans. Is Bacteria Good? Bacteria are the primary recyclers of materials in the environment, particularly nitrogen. Newsflash!!! There was bacteria discovered that can do photosynthesis! Is Bacteria Good? Bacteria are also essential for many processes we depend on – sewage treatment, cheese production, antibiotic production, and biotechnological processes like gene cloning and protein production. Bacteria are used to produce insulin and other drugs that people need. The Domain Eukarya is divided into 4 Kingdoms: Protista Fungi Plantae Classifying Critters activity Animalia PROTISTS • Protists are eukaryotes because they all have a nucleus. • Many have chloroplasts with which they carry on photosynthesis. • Many are even unicellular . A better name for Protists would be "Eukaryotes that are neither Animals, Fungi, nor Plants". Protists Visit Protist Park FUNGI Fungi sometimes look like plants, but they’re not! Fungi can’t do photosynthesis, because they don’t have chloroplasts; they get their nutrients from the organic material they live in. Decomposers, like mushrooms, feed on dead organic material. Some fungi feed on living organisms, such as plants, animals and even other fungi. This causes diseases and infections in these organisms (like athlete’s foot and ringworm in humans). Other differences from plants: • fungi don’t have roots • fungi’s cell walls are made of chitin, not cellulose. FUNGI ANIMALS Invertebrates (no backbone) Vertebrates (backbone) Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family Genus Species Remember: Kids Prefer Candy Over Fresh Green Salad Class Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Chordata Class: Mammalia Order: Carnivora Family: Felidae Genus: Panthera Species: Tigris Subspecies Panthera tigris altaica Siberian or Amur Tiger, Southeast Russia/China Panthera tigris tigris India Panthera tigris amoyensis Southern China Panthera tigris corbetti Indochina Panthera tigris sumatrae Sumatran Tiger, Sumatra DO NOW-Grade Level V: 0 Tuesday Answer on page 60 of your INB… April 8, 2014 What land formation is in the following topographic maps? A. B. C. DO NOW- Pre-AP V: 0 Tuesday Answer on page 60 of your INB… April 8, 2014 What land formation is in the following topographic maps? A. B. C. When finished, add APE MAN, RUBIES, and labels to the periodic table to your reference materials page. Homework & Agenda Homework Homework: STAAR Review Today’s Agenda -5 Kingdom Notes -Body Systems Card sort -BrainPop: Body Systems -Finish Cell Analogies V: 0 TEKS V: 0 - Recognize levels of organization in plants and animals, including cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, and organisms Vocabulary Heterotrophic Autotrophic Unicellular Multicellular V: 0 Prokaryotic Eukaryotic Asexual Sexual EQs & Objectives ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS: DAILY OBJECTIVES: Students will… -Classify organisms into their appropriate Kingdoms. V: 0 Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Prokaryotic “Pro” rhymes with NO! Has NO Nucleus V: 0 Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Eukaryotic “You have one”! Cytoplasm Cell Membrane Nucleus Has a Nucleus V: 0 Unicellular vs. Multicellular Unicellular Or “uno-cellular” 1 An organism made of only 1 cell. V: 0 Unicellular vs. Multicellular Multicellular “Multiple, Many” An organism that is made of many cells. V: 0 Autotrophic vs. Heterotrophic Autotrophic Makes its own food from sunlight. (plants) V: 0 Autotrophic vs. Heterotrophic Heterotrophic Eats food to gain nutrients. Gets its food from other sources. “Head”erotrophic V: 0 Sexual vs. Asexual Sexual Reproduction Takes 2 organisms to produce a new one. V: 0 Sexual vs. Asexual Asexual Reproduction Alone V: 0 One organism “clones” itself to produce a new organism. Body Systems V: 0 Body Systems BrainPop Video V: 0 DO NOW-Grade Level V: 0 Tuesday Answer on page 60 of your INB… April 8, 2014 What land formation is in the following topographic maps? A. B. C. DO NOW- Pre-AP Wed/ Thurs April 9 & 10, 2014 V: 0 Add APE MAN, RUBIES, and labels to the periodic table to your reference materials page. Homework & Agenda Homework Homework: STAAR Review Today’s Agenda -Finish Body Systems -Review Stations V: 0 EQs & Objectives ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS: DAILY OBJECTIVES: Students will… -Classify organisms into their appropriate Kingdoms. V: 0 Body Systems • Card Sort and Record in Table V: 0 Body Systems BrainPop Video V: 0 Stations • • • • Station 1: PE and KE, F=ma Station 2: Convection Station 3: Plate Tectonics Station 4: Weather Maps