* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cells A cell is the basic unit of structure and function in all living
Survey
Document related concepts
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
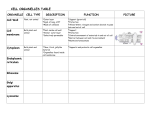
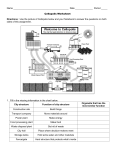
Cells A cell is the basic unit of structure and function in all living organisms. Cells arise from pre-existing cells. All living organisms are composed of one or more cells. Unicellular Organisms Multicellular Organisms Cells contain organelles. Organelles are structures within the cell that have a specific function. Examples of organelles include: Prokaryotic Cells vs. Eukaryotic Cells The organelles in a cell have specific jobs, and their activities are coordinated to maintain homeostasis. Not all cells have all the same organelles. Example: Chloroplasts Organelle and Physical Description Function Life Process performed by organelle Other Information Cytoplasm Contains many dissolved substances such as: Cell Membrane (Plasma Membrane) The cell membrane is semi-permeable, which means that only certain substances can move into or out of the cell. Nucleus Only present in eukaryotic cells. The DNA of prokaryotic cells floats freely in the cytoplasm. The chromosomes (DNA) contain the genetic information (genes) of the cell or organism. DNA contains hereditary information, instructions for protein synthesis and controls the actions of the cell. Organelle and Physical Description Function Life Process performed by organelle Other Information Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum SER is like a conveyor belt Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum RER is like an assembly line at a factory. Ribosomes Assembles amino acids to form proteins. Composed of rRNA Mitochondria The MIGHTY Mitochondrion is the powerhouse of the cell Aerobic Respiration: C6H12O6 + 6 O2 Æ Energy + 6 H2O + 6 CO2 Organelle and Physical Description Chloroplasts Function Life Process performed by organelle Other Information Photosynthesis 6 H2O + 6 CO2 Æ C6H12O6 + 6 O2 Golgi Bodies (Golgi Apparatus) The golgi bodies are like FedEx or UPS for the cell. Vacuoles Special kinds of vacuoles: Contractile vacuoles, Large Central Vacuole and Plastids Lysosomes Lysosomes break down food, worn out organelles or pathogens using hydrolytic enzymes. Organelle and Physical Description Function Life Process performed by organelle Other Information Centrioles Only found in animal cells. Not present in plant cells. Flagella & Cilia Flagella and cilia are extensions of the cytoskeleton that go beyond the cell membrane. Cytoskeleton Composed of protein formed into microtubules. Provides a scaffold to move organelles and materials around inside the cell. Cell Wall Cell walls will exist after a cell dies. Other organelles break down, the cell wall does not. Composed of a complex carbohydrate called cellulose.