* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plate Tectonic Terms
Survey
Document related concepts
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Geomorphology wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
Oceanic trench wikipedia , lookup
Abyssal plain wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Mantle plume wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
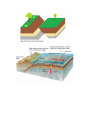
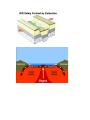
Plate Tectonic Terms 1. Plate Tectonics - The theory that the Earth's crust and upper mantle (the lithosphere) is broken into a number of more or less rigid, but constantly moving, segments or plates. 2. Pangea, also spelled Pangaea, in early geologic time, a supercontinent that incorporated almost all the landmasses on Earth. 3. Fault - A weak point in the Earth's crust and upper mantle where the rock layers have ruptured and slipped. Faults are caused by earthquakes, and earthquakes are likely to reoccur on pre-existing faults. 4. Lithosphere - outer solid part of the earth, including the crust and uppermost mantle. The lithosphere is about 100 km thick, although its thickness is age dependent (older lithosphere is thicker). 5. Mid-Ocean Ridge - an underwater mountain system that consists of various mountain ranges (chains), typically having a valley known as a rift running along its spine, formed by plate tectonics. 6. Ocean Trench - The oceanic trenches are hemisphericscale long but narrow topographic depressions of the sea floor. They also are the deepest parts of the ocean floor. Trenches define one of the most important natural boundaries on the Earth’s solid surface, that between two lithospheric plates. 7. Rift - a linear zone where the Earth's crust and lithosphere are being pulled apart. 8. Rift Valley - a linear-shaped lowland between several highlands or mountain ranges created by the action of a geologic rift or fault 9. Seafloor Spreading - a process of plate tectonics where new oceanic crust is created as large slabs of the Earth's crust split apart from each other and magma wells up to fill the gap.