* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell structure student notes PreAP 14-15
Survey
Document related concepts
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
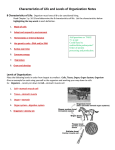
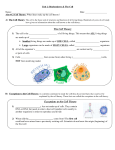
Characteristics of Life and Levels of Organization Notes 8 Characteristics of Life: Organism must have all 8 to be considered living. Read Chapter 1 p. 16-19 and determine the 8 characteristics of life. List the characteristics below highlighting the key words in each definition. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Levels of Organization: Place the following levels in order from largest to smallest: Cells, Tissue, Organ, Organ System, Organism Give an example for each using yourself as the organism and working your way down to cells Ex: Organism – Jeremy Lin down to Cell—stomach muscle cell 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Cell Structure and Function Notes Discovery of the Cell: Mid 1600’s scientists began using microscopes to observe living things ____________ ___________ used microscope to observe thin slice of ________—dead plant material Cork seemed to be made of box-like chambers—Hooke called ___________ Anton van Leeuwenhoek discovered _____________ _____________ in pond water Cell Theory: All living things composed of __________ Cells are the basic unit of ________________ and ________________ in living things New cells are produced from _______________________ ____________ Cell and its Environment: Organisms made of one cell—_____________________ organisms Ex: ____________________ Organisms made of many cells—______________________ organisms Ex: ___________________________________ Each cell must be in “_______________” with its environment, exchange food, waste, H2O, CO2, O2 etc. Process by which organisms maintain a relatively stable internal environment—___________________ Cell: Organisms that do not have a distinct nucleus—_______________________ (PRO = BEFORE) Ex: _____________________ Organisms with cells that have true nucleus and organelles—_______________________ (EU = TRUE) Ex: __________________________________________ Cell Parts and Their Functions: Specialized cell parts called __________________________—“little organs” 1. ___________ _______________________—determines what goes in and out of the cell 2. _________________________—gel-like medium that holds the organelles in position 3. ______________________—control center of the cell Double membrane that surrounds the nucleus—______________ _________________ Hereditary information inside the nucleus—_________________________ (DNA) Site where ribosomes are made--___________________ 4. _______________________—makes proteins 5. _____________ ___________________ ________________________ (rough ER)—makes and transports proteins within the cell Called rough ER because of the _____________________ found on its surface 6. _____________ ___________________ ________________________ (smooth ER)—makes and transport lipids and other materials within the cell Called smooth ER because _____ ________________________ found on its surface 7. _________________________—network of protein filaments that helps cell maintain its shape 8. _______________ ________________________—processes and packages proteins and other substances produced in the ER Golgi apparatus prepares these substances either to be stored in the cell or secreted outside the cell in membrane bound _______________ 9. _________________________—supplies energy to the cell (powerhouse) 10. ______________________—sac-like structures for storage of materials such as water, salts, proteins and carbohydrates Plant cells usually contain a _______________ _________________ that fills most of the cell—pressure from this large vacuole helps plants support themselves Found in animal cells only: 11. ______________________—cleans up the cell and digests unwanted materials, contains digestive enzymes Found in plant cells only: 12. __________ ____________—provides support and protection for cell Composed mainly of ___________________ (plant starch)—_____________ for our diet 13. ___________________—makes glucose using the energy from the sun (__________________) Specialized Parts for movement: 1. ________________ (like little hairs) 2. __________________ (like a tail) Specialized Cells: Different cells in your body do different jobs. The ___________________ (how it’s built) of cells matches the ______________________ (what it does). Plant Examples: 1. Leaf cell—contains __________ ___________________ to maximize ________________________ 2. Root cell (potato)—contains __________ _______________ to maximize water and starch storage Animal Examples: 1. Epithelial cells—have __________ to increase ______________ _________________________; found in the intestines 2. Muscle cells—contain ________ _____________________ to produce more energy for movement 3. Nerve cells—have fibers called ____________________ that allow nerve cells to __________________________ with each other Cell Membrane: (text p. 182) 1. ______ cells have a cell membrane 2. Cell membranes are _____________________________________________ control what enters and leaves the cell not solid, but fluid—______________________________________________ 3. Composition – ______________________________________ Phospholipid bilayer—_________________________________________________ ex: O2, CO2, H20, alcohol Proteins—embedded in lipids, allows for passage of __________________________________ __________________________________________ a. _____________________________ – has a unique _____________________________ to identify the cell – how organ donors and recipients are matched b. _____________________________ – allows __________________________________ needed by the cell to pass through the cell membrane c. _____________________________ – allows cell to communicate with outside environment d. _____________________________ – helps keep membrane fluid and stable VIRUSES (Latin for poison) text p.478 A. General Characteristics 1. A virus is an infectious agent made up of – a. they have no nucleus, no organelles, no cytoplasm or cell membrane – b. viruses have either – 2. Viruses are - organism that depends entirely upon another living organism (host) for its existence in such way that it harms that organism. B. Examples: 1. Bacteriophage – 3. Ebola 4. Common Cold 5. HIV 6. Herpes 7. H1N1 8. Avian Flu 2. Flu (influenza) Viruses: Based on the characteristics of life and the general characteristics of a virus, are viruses considered dead or alive? Explain in the space below.