* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ch 21: Cardiovascular System - The Heart -
Saturated fat and cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Remote ischemic conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
History of invasive and interventional cardiology wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
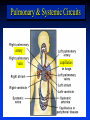
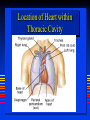
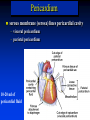
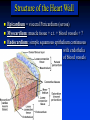
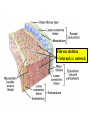
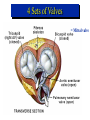
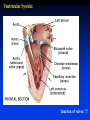
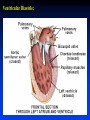
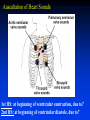
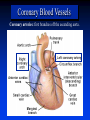
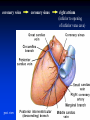
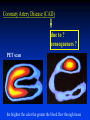
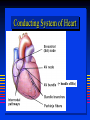
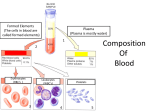
Ch 21: Cardiovascular System - The Heart - Pulmonary & Systemic Circuits artery vein capillaries Location of Heart within Thoracic Cavity Pericardium serous membrane (serosa) lines pericardial cavity – visceral pericardium – parietal pericardium 10-20 ml of pericardial fluid Structure of the Heart Wall Epicardium = visceral Pericardium (serosa) Myocardium: muscle tissue + c.t. + blood vessels + ? Endocardium: simple squamous epithelium continuous with endothelia of blood vessels Cardiac Muscle difference to skeletal muscle?? Intercalated Discs • Desmosomes & • Gap Junctions functional syncytium = fused mass of cells Fibrous Skeleton Lots of collagen and elastic fibers in the connective tissue of the heart. function:? support (eg: fibrous rings supporting valves) prevents over-expansion elasticity helps to return to original shape physical separation of atria from ventricles Fibrous skeleton = internal c.t. network Surface Anatomy of Heart Auricle of atria (expandable) Coronary sulcus (between atria & ventricles) Ant. & post. interventricular sulcus Base (3rd costal cartilage) vs. apex (5th intercostal space) Vessels entering & leaving the heart Sectional (Internal) Heart Anatomy Atria & ventricles Interatrial & interventricular septae Valves (fibrous tissue) Pectinate muscles (auricles & ant. atria) Trabeculae carneae (ventricles) Chordae tendinae & papillary muscles Left vs. Right Ventricle Left: high pressure pump Right: low pressure pump ventricular contraction also functions as “suction pump” 4 Sets of Valves = Mitral valve Mitral Valve Prolapse Most common cardiac variation (~ 10% of population) Mitral valve cusps do not close properly Regurgitation during left ventricular systole How can you diagnose? Not life threatening; may be life-stile threatening Ventricular Systole: function of valves: ?? Ventricular Diastole: Auscultation of Heart Sounds: 1st HS: at beginning of ventricular contraction, due to? 2nd HS: at beginning of ventricular diastole, due to? Coronary Blood Vessels Coronary arteries: first branches off the ascending aorta. coronary veins post. view coronary sinus right atrium (inferior to opening of inferior vena cava) Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) due to ? consequences ? PET scan the brighter the color the greater the blood flow through tissue Myocardial Infarction (MI) = Heart attack Ischemic tissue degenerates area = infarct nonfunctional Most commonly due to severe CAD (coronary thrombosis) ~ 1.3 Mio MIs / year in US Predisposing factors? Conducting System of Heart (= bundle of His) Cardiac Cycle, EKG, Autonomic Control of Heart Rate covered in Physiology the end