* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Heart Physiology Cardiac Conduction System Electrical System
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Atrial fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
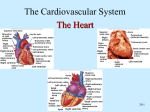
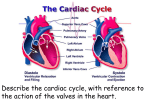
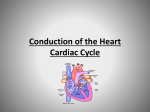
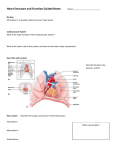
Heart Physiology Cardiac Conduction System · ability of cardiac muscle to depolarize and contract is intrinsic Heart Physiology does NOT depend on nervous system composed of autorhythmic cells 1. pacemaker potential 2 3 1 2. depolarization no stable resting potential instead, Na+ channels are opened after hyperpolarization allowing potential to drift toward threshold threshold potential = -40mV Ca2+ channels open and Ca2+ rushes into cells 3. repolarization K+ channels open and K+ rushes out of cell Changing the Rhythm Electrical System · cardiac center located in the medulla oblongata 1. Sinoatrial (SA) node pacemaker determines heart rate 70-80 per minute 1 2. Atrioventricular (AV) node 4 impulse pauses about 0.1 sec to allow atria to finish contracting 3 3. Atrioventricular bundle 5 electrical connection between atria and ventricles 4. R and L bundle branches 5. Purkinje fibers 2 sympathetic nervous system speeds up heart rate and force (cardioacceleratory center) parasympathetic nervous system slow down heart rate and force (cardioinhibitory center) · factors that affect heart rate anxiety/stress and activity speed up rate meditation, yoga, sleep slow down rate 4 highly branched responsible for ventricular contraction In a healthy heart, it takes 0.22 sec from SA node stimulation to end of ventricular depolarization! Electrocardiogram (ECG) · aka electrokardiogram (EKG) · recording of the electrical changes in the myocardium · P wave - atrial depolarization Arrhythmias tachycardia quickly followed by atrial contraction · QRS complex - ventricular depolarization quickly followed by ventricular contraction atrial repolarization obscured by QRS complex fibrillation · T wave - ventricular repolarization bradycardia Heart Physiology Heart Sounds · associated with closing valves · lub-dub, pause, lub-dub, pause, and so on lub - AV valves (tricuspid and bicuspid) close dub - SL valves (pulmonary and aortic) close pause - heart resting between beats Cardiac Cycle · aka "heartbeat" · mechanical actions of the heart · each heartbeat (cycle) blood is forced out of ventricles · average adult pumps about 5 L/min · stroke volume - volume of blood pumped by each ventricle per heartbeat · cardiac output - volume of blood pumped per minute by the heart (both ventricles) multiple stroke volume (mm) by heart rate (beats/min) Cardiac Cycle (cont.) · systole - contraction of heart muscle · diastole - relaxation of heart muscle · steps 1. atria contract forcing blood into relaxed ventricles (AV valves open, SL valves closed) 2. ventricles contract forcing blood into pulmonary trunk and aorta (AV valves closed; SL valves open) 3. both atria and ventricles relax and atria begin to fill passively with blood (all valves closed) Cardiac Cycle