* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Cardiac Cycle
Survey
Document related concepts
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Atrial fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
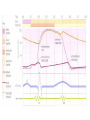
The Cardiac Cycle Aim: To understand the Cardiac Cycle Heart Beat • A single heart beat is known as the cardiac cycle. • Atrial Systole is where both atria contract (0.1s) • Ventricular Systole is where both ventricles contract forcing blood through the pulmonary artery to the lungs and through the aorta to the rest of the body (0.3s) • Atrial diastole is where the atria relax. Blood will enter the atria from the large veins (0.7s) • Ventricular diastole is where the ventricles relax, and start to fill with blood from the atria as the next cycle begins (0.5s) • Cardiac Cycle Animation Stroke Volume and Cardiac Output • Stroke volume is the volume of blood pumped by the heart in one cardiac cycle. • Typically about 80cm3. • Stroke volume increases during exercise. • Cardiac Output is the volume of blood pumped in one minute. It is calculated by multiplying the stroke volume by the heart rate. It is expressed in litres of blood per minute. Factors Affecting Heart Rate • • • • Adrenaline. Movement of limbs (stretch receptors) Levels of respiratory gases in the blood Blood pressure – if it gets too high a safety mechanism prevents heart rate increasing further.