* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Heart SLIDES - Penguin Prof Pages
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
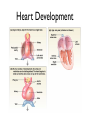
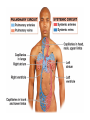
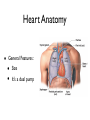
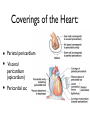
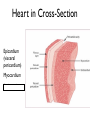
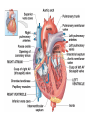
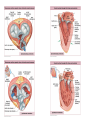
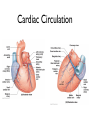
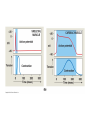
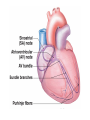
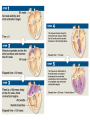
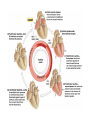
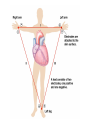
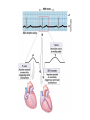
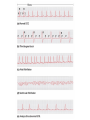
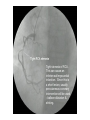
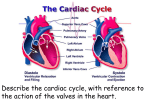
Cardiovascular System: The Heart Heart Development I. Introduction Functions of the Cardiovascular System: • • • Transportation: • • • • Respiratory gasses Nutrients Waste Hormones Regulation of temperature Protection (immune system) Components of the Cardiovascular System • Cardiovascular System = heart and the vessels • Lymphatic system = lymph vessels, lymph nodes, lymph organs Heart Anatomy • General Features: • • Size It's a dual pump Coverings of the Heart: • • Parietal pericardium • Pericardial sac Visceral pericardium (epicardium) Heart in Cross-Section Epicardium (visceral pericardium) Myocardium Endocardium Chambers of the Heart • • • Atria receive blood Ventricles pump blood • Right ventricle pumps blood to the pulmonary circuit • Left ventricle pumps oxygenated blood to the systemic circuit NOTE: Arteries Always carry blood Away from the heart Heart Valves • • Atrioventricular(AV) valves prevent backflow from ventricles to atria • • • Tricuspid valve Bicuspid valve (mitral valve) Chordae tendineae originate from papillary muscles Semilunar valves • • Aortic semilunar valve Pulmonary semilunar valve Cardiac Circulation Electrical Events in the Heart Compare and Contrast Skeletal vs. Cardiac Muscle • • • • • • Purpose Basic principles (all-or-none) Time Summation / Tetanus Refractory period Source of stimulus / role of NS Extrinsic Regulation Autonomic nervous system • • Sympathetic system Parasympathetic Intrinsic regulation (nodal system) • • • • • Sinoatrial (SA) node contains pacemakers Atrioventricular (AV) node Atrioventricular bundle (Bundle of His) Bundle branches Purkinje fibers The Cardiac Cycle • Cardiac cycle = contraction, relaxation cycle of the heart • • • Systole = contraction • Cardiac Output = heart rate x stroke volume Diastole = relaxation Stroke volume = volume of blood ejected by a ventricle as it contracts The Cardiac Cycle • • 1. Atrial and Ventricular Diastole • Atria are filling with blood, AV valves are open and blood passively fills the ventricles. 2. Early Ventricular Systole • Ventricles begin to contract, forcing the AV valves to close • Isovolumic ventricular contraction: ventricles contract, but AV and semilunar valves are closed The Cardiac Cycle • • 3. Ventricular Systole and Blood Ejection • When ventricular contraction generates enough pressure to open the semilunar valves, blood enters the arteries 4. Ventricular Diastole • • Ventricles relax, pressure decreases • Blood flows back into the heart, closing the semilunar valves Blood remaining in ventricles is called end-diastolic volume, EDV Electrocardiogram (ECG) • • P wave = atrial depolarization • T wave = repolarization of ventricles QRS wave = depolarization of ventricles (and repolarization of atria). Arteriosclerosis and Cardiac Arrhythmia • Plaques can clog the arteries, causing restricted blood flow • Smoking, hypertension, and a diet high in cholesterol and fats contribute • • • High ratio of HDL to LDL is desirable Myocardial ischemia Myocardial infarction = heart attack. Tight stenosis of RCA. This can cause an inferior wall myocardial infarction. Since this is a short lesion, usually percutaneous coronary intervention will be used - balloon dilatation & stinting. Cardiac Arrhythmias • Arrhythmias • • • Bradycardia = heart rate less than 60 beats/ min • • Fibrillation = rapid, uncontrolled contractions Tachycardia = heart rate more than 100 / min Flutter = rapid, controlled contractions of atria or ventricles Electrical defibrillation can sometimes re-regulate the myocardial cells to become synchronous again.