* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nervous System PPT
Brain–computer interface wikipedia , lookup
Human multitasking wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
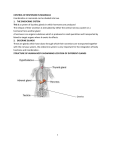
Neurogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry of Alzheimer's disease wikipedia , lookup
Functional magnetic resonance imaging wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Neurotechnology wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Sports-related traumatic brain injury wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
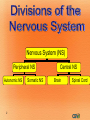
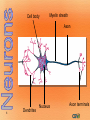
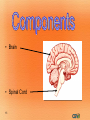
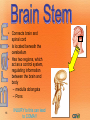
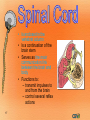
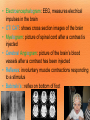
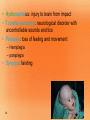
1 Nervous System (NS) Peripheral NS Autonomic NS 2 Somatic NS Central NS Brain Spinal Cord What is the nervous system? Each day, you use verbal and nonverbal communication as a signal to others. For example, to signal a student has a question, he/she would raise his/her hand. The teacher would recognize this signal and direct his/her attention to the student. Your body works in much the same way. The nervous system is one of your body’s personalized communication systems. Signals are sent from one location to another in order to control and coordinate many bodily functions. The nervous system responds to internal and external stimuli. 3 • Are cells, which transmit electrical signals or impulses • Provide a pathway for messages going to and from the brain and spinal cord 4 • Characteristics: – have a cell body, which is the largest part – have processes » are fiber-like extensions » increase the distance at which signals can be transmitted » two types of processes: dendrites -- carries signal to the cell body axons -- carries signal away from cell body 5 Cell body Myelin sheath Axon 6 Dendrites Nucleus Axon terminals • • • • 7 Transmit signals toward the body Are short and branch extensively Neurons may have dozens of dendrites Are bound with axons to form a nerve pathway • Transmit signals away from the body • Most neurons have only one very long axon • Gaps between synaptic knobs are called synapses 8 • Myelin sheath » cover the axon for protection » aid in delivery of impulses traveling through the axon by insulating the nerve 9 • Is the location where neurons transfer impulses between cells • Are gaps separating the axon terminal from dendrites of adjacent cell • Have terminals containing sacs filled with neurotransmitters – are chemicals used by neurons to transmit impulses across a synapse to another cell 10 1. Central nervous system • central processing system of the nervous system -- much like the main processing chip of a computer 2. Peripheral nervous system • relays information received from the central nervous system to organs and glands 11 12 • Brain • Spinal Cord 13 • Is the central control unit for the body • Is protected by the skull – cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) occupies space between two layers » functions as a shock absorber » allows for the exchange of nutrients and waste between blood and nervous tissue 14 • Divided into: – cerebrum – cerebellum – brain stem Did you know the average adult human brain weighs about 3 lbs.? 15 • Connects brain and spinal cord • Is located beneath the cerebellum • Has two regions, which act as a control system, regulating information between the brain and body – medulla oblongata – Pons 16 INJURY to this can lead to COMA!! • Is enclosed in the vertebral column • Is a continuation of the brain stem • Serves as the main communication link between the brain and body • Functions to: – transmit impulses to and from the brain – control several reflex actions 17 18 Divided into two parts: 1. Motor Division – relays impulses from the central nervous system to muscles and glands 2. Sensory Division – 19 relays impulses from sensory organs to the central nervous system 20 • Electroencephalogram: EEG, measures electrical impulses in the brain • CT/ CAT: shows cross section images of the brain • Myelogram: picture of spinal cord after a contrast is injected • Cerebral Angiogram: picture of the brain’s blood vessels after a contrast has been injected • Reflexes: involuntary muscle contractions responding to a stimulus • Babinski’s : reflex on bottom of foot 21 22 • Concussion: injury to brain from impact • Coma: abnormal deep sleep wit or no response to stimuli • Brain contusion: bruise to brain • Shaken baby syndrome: closed head trauma; brain hitting skull • Alzheimer’s: degeneration of neurons in the brain • Amnesia: loss of memory • CVA: stroke, cerebrovascular accident; lack of o2 to brain • Epilepsy: seizure; abnormal electrical impulse – Aura: the feeling before a seizure 23 • Hydrocephalus: injury to brain from impact • Tourette syndrome: neurological disorder with uncontrollable sounds and tics • Paralysis: loss of feeling and movement – Hemiplegia – paraplegia • Syncope: fainting 24