* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download WS 8 – 3: Translation and Protein Synthesis Name
Transformation (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
RNA polymerase II holoenzyme wikipedia , lookup
Real-time polymerase chain reaction wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
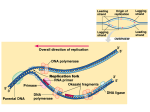
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Transfer RNA wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
WS 8 – 3: Translation and Protein Synthesis Name_________________________________________________ For the questions 1 - 4, use the DNA molecule below. TACCGCTAGGATACGTGCAAATTAATT 1. What mRNA sequence molecule would be made from the strand of DNA above? AUGGCGAUCCUAUGCACGUUUAAUUAA 2. What tRNA sequence would be complementary to the mRNA molecule produced above? UACCGCUAGGAUACGUGCAAAUUAAUU 3. Use the genetic code in your book to tell which amino acids are formed from this molecule. METH – ALA – ISOLEU – LEU – CYS – THR – PHE – ASP - STOP For the questions 4 - 6, use the DNA molecule below. TACGGGCCCAAATTTTGGACTCATCTAATT 4. What mRNA sequence molecule would be made from the strand of DNA above? AUGCCCGGGUUUAAAACCUGAGUAGAUUAA 5. What tRNA sequence would be complementary to the mRNA molecule produced above? U A C G G G C C C A A A U U U U A C A C U C A U C U A A UU 6. Use the genetic code in your book to tell which amino acids are formed from this molecule. METH – PRO – GLY – PHE – LYS – THR – STOP – VAL - ASP ACID - STOP For the questions 7 - 9, use the DNA molecule below. TACAATCCGTTATGCCACTCATGATTAGAGTCGCGGGATT 7. What mRNA sequence molecule would be made from the strand of DNA above? AUGUUAGGCAAUACGGUGAGUACUAAUCUCAGCGCCCUAA 8. What tRNA sequence would be complementary to the mRNA molecule produced above? UACAAUCCGUUAUGCCACUCAUGAUUAGAGUCGCGGGAUU 9. Use the genetic code in your book to tell which amino acids are formed from this molecule. METH – LEU – GLY – ASP – THR – VAL – SER – THR – ASP – LEU – SER – ALA – LEU 10. How many codons are in the above mRNA molecule? 13 11.__Transfer RNA (tRNA)___type of RNA that transfers amino acids to the ribosome for protein assembly 12.___________AUG________________known as the initiator codon 13._________Genetic code_____________________set of instructions that DNA and RNA use to make proteins 14.________Anticodon____________________the 3 nucleotide sequence in tRNA that is complementary to mRNA. 15._______Translation_________________________process by which mRNA is decoded into a protein 16._____Polypeptide (protein)________________________name for a group of amino acids bonded together 17.______UAG, UGA, UAA ____________________________name for the 3 stop codons 18.______Ribosomes________________________place in the cell where translation takes place (be specific) 19. Explain why DNA and mRNA are read 3 nucleotides at a time? DNA and mRNA are read three nucleotides at a time in order to provide enough information to code for the twenty essential amino acids that the human body needs. If one base coded for one amino acid, that would only provide enough information to code for four amino acids. If two bases equaled one amino acid, that would only provide enough information to code for sixteen amino acids. 20. Explain the entire process of how DNA contains the code to make proteins such as hemoglobin or a protein that controls what color your hair or eyes are. In your answer you should include information about the structure of DNA, the process of transcription, and translation and protein synthesis. DNA is the molecule of life. It contains genes that provide the code to make proteins that control an organism’s functions. It is shaped like a double helix which allows it to replicate itself. Once it divides, each cell will have identical DNA and function the same way. If the body needs to make a particular protein in order to function, it makes a copy of the section of DNA that it needs. This process is called transcription and a molecule called messenger RNA (mRNA) is made. Transcription takes place in the nucleus and once mRNA is made, it leaves the nucleus and heads to the ribosome in order to be translated into a protein. Once at the ribosome, translation begins. During translation, another RNA molecule called transfer RNA (tRNA) is involved. tRNA reads the codon of mRNA and picks up the correct amino acid in the cytoplasm and transfers it to the ribosome and matches its anticodon with the codon of mRNA. tRNA continues to read each codon of mRNA and bring the correct amino acid to the ribosome. At the ribosome, ribosomal RNA (rRNA) connects one amino acid after another and joins them with a peptide bond. This process repeats itself until the stop codons are reached. Once they are reached, a polypeptide is made. 21. Where does process A take place in the cell? nucleus 22. What is the process represented by A? transcription 23. What is the process represented by B? translation 24. Complete the table below: Original DNA code mRNA copy tRNA anticodon Amino Acid TGA GTT OR GTC AAA CAA ACC ACU CAA OR CAG UUU GUU UGG UGA GUU OR GUC AAA CAA ACC Threonine Glutamine PHENYLALANINE VALINE Tryptophan