* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 16 Review
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Dual inheritance theory wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Genetic testing wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
Down syndrome wikipedia , lookup
DiGeorge syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
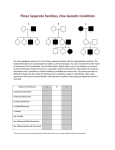
Review: Biology 3201 Chapter 16 Genetics 1. Explain how Mendel’s experiments support each of the following: (i) Principle of Dominance (ii) Law of Segregation (iii) Law of Independent Assortment 2. Relate the process of meiosis to Mendel's laws of segregation and independent assortment. 3. Explain how the work of Walter Sutton lead to the chromosome theory of inheritance 4. State the chromosome theory of inheritance. 5. How did the Chromosome Theory of Inheritance affect the understanding of Mendel’s Law of Independent Assortment? 6. Understand how Morgan’s experiments with Drosophila lead to our understanding of traits that are sex linked. 7. Why are sex linked traits more common in males? 8. What are polygenic traits, give two examples of these types of traits in humans. 9. Know how to use the product rule to predict probabilities of consecutive events. 10. You MUST know how to carry out all types of crosses that we have done. Monohybrid (single trait) multiple alleles Dihybrid (two trait) sex-linkage co - dominance test cross incomplete dominance 11. distinguish among the different types of chromosome mutations Include: (i) deletion (ii) duplication (iii) inversion (iv) translocation (v) nondisjunction (monosomy, trisomy) 12.Identify in general terms the impact of genetic diseases on the homeostasis of an organism – describe several examples of human genetic diseases caused by chromosomal mutations. Include: (i) Down syndrome (ii) Turner syndrome (iii) Klinefelter syndrome (XXY syndrome) (iv) Jacobs syndrome (XYY syndrome) (v) Triple X syndrome 13. Interpret patterns and trends in genetic data – analyze and interpret models of human karyotypes 14. identify in general terms the impact of genetic diseases on the homesostasis of an organism and explain the circumstances that lead to genetic diseases Include: (i) autosomal recessive inheritance (Tay Sachs, PKU) (ii) co-dominant inheritance (Sickle Cell Anemia) (iii) autosomal dominant inheritance (Progeria, Huntington’s) (iv) incomplete dominant inheritance (FH) (v) x-linked recessive inheritance (color blindness, Muscular Dystrophy, Hemophilia)