* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Mendelian and Human Genetics Standard Learning Target I can
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Pathogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Dual inheritance theory wikipedia , lookup
Human genome wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Genetic testing wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
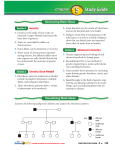
Name: _____________________ Mendelian and Human Genetics Chapter 11.1-11.3, 14.1-14.2 How Do I Feel? Standard 1. Determine how an organism passes its characteristics on to its offspring. (11.1) 2. Predict the outcome of genetic crosses. (11.2) 3. Determine how different factors can affect an organism’s traits. (11.3 & 14.1) 4. Analyze how studying the human genome explains how traits are inherited (14.1). 5. Explain causes of genetic disorders (14.2). Learning Target I can…. A) Describe Mendel’s studies and conclusions about inheritance. B) How does an organism get its unique characteristics? C) Explain how different forms of a gene are distributed to offspring. A) How do geneticists use the principles of probability to make predictions about inheritance? o Create a punnett square showing a cross between a tall heterozygous pea plant and a short pea plant- give the phenotype and genotype expected B) Explain the principle of independent assortment. A) Describe the patterns of inheritance of human traits. Give an example using a punnett square for each pattern: • Dominant vs. recessive, Incomplete dominance, Codominant, Multiple alleles, Polygenes, Sex linked, & X-chromosome in activated B) Explain how the environment plays a role in how genes determine traits. C) Explain what a chi-square analysis is and how it compares to observed to predicted data. A) What is a karyotype? B) Identify the types of chromosomes in a karyotype. C) Draw a pedigree of your own family using a trait (i.e. tongue rolling, eye color, hair color) A) Explain how small changes in DNA cause genetic disorders. Do genetic disorders have advantages? B) Summarize the problems caused by nondisjunction. C) Explain the how genetic disorders can be detected. 1. = I know this stuff! 2.= I could use some help... 3. = Ahh! What is this? Terms Initial • • • • • • • • • • • Genetics Fertilization Trait Hybrid Genes Probability Homozygous Heterozygous Phenotype Genotype Punnett Square • • • Alleles Principle of dominance Segregation • Gametes • • • • • • • • Independent assortment Monohybrid cross Dihybrid cross Incomplete dominance Codominance Multiple alleles Polygenic traits Sex-linked genes • Pedigree • p2 + 2pq + q2 = 1 • p+q=1 • • • • Genome Karyotype Sex chromosomes Autosomes • nondisjunction Final