* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Cardiac Cycle Cardiac conduction system Cardiac Muscle
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Cardiothoracic surgery wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Ventricular fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
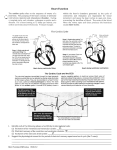
The Cardiac Cycle Bio 250 Laboratory Exercise Cardiac conduction system This system, composed of specialized cardiac muscle tissue, initiates and conducts depolarization waves though the myocardium. Impulses from the S-A node pass slowly to the A-V node; impulses travel rapidly along the A-V bundle and Purkinje fibers. Cardiac Muscle (Myocardium) Muscle fibers in the ventricular walls are arranged in whorls that squeeze blood out of the contracting ventricles. 1 1 Some Terminology Systole- contraction and pumping phase of the cardiac cycle Diastole- relaxation and filling phase of the cardiac cycle Atrial and ventricular systole alternate with each other The electrocardiogram P-wave occurs as the atria depolarize QRS-complex occurs as the ventricles depolarize T-wave occurs as the ventricles repolarize P-R Interval extends from beginning of Pwave to the beginning of the QRS-complex Q-T Interval extends from the end of the PR Interval to the end of the T-wave 2 2 ECGs, Normal & Abnormal No P waves ECGs, Abnormal Arrhythmia: conduction failure at AV node No pumping action occurs 3 3 Physiograph Physiograph will measure: Electrocardiogram- electrical activity of the heart and its conduction system Heart Sounds- sounds made as the AV and SL valves close Pulse Pressure- rising pressure during ventricular systole and falling pressure during ventricular diastole Dicrotic notch- blood rebounding off SL valves as they close ECG Einthoven’s Triangle Standard Leads I II III 4 4 Heart Sounds Microphone Plethysmograph Subject wired to ECG, heart microphone and plethysmograph 5 5 Cardiac Cycle 6 6 Things to Remember Plethysmogram- pressure rises during systole (contraction) of the ventricle and falls during diastole (relaxation). Electrocardiogram P wave represents the action potential that passes over the atria and causes atrial systole. QRS complex wave represents the action potential that passes over the ventricles and causes ventricular systole. Continued Heart Sounds The first heart sound occurs when the AV valves (tricuspid and mitral) close at the beginning of ventricular systole The second heart sound occurs when the SL valves (aortic and pulmonic) close at the end of ventricular systole 7 7