* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Organelle Notes
Survey
Document related concepts
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
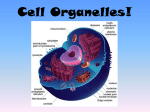
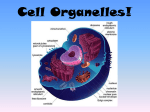
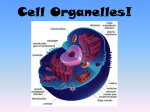
Class Notes Cell Organelles Questions/Main Idea: What is an organelle? What is the function of the ell membrane? What is the function of the cell wall (plants)? What is the function of the nucleus? Name: _______________________________________ Period:_______________________________________ Date: _______________________________________ Notes: • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • What is the function of the nucleolus? What is the function of the cytoplasm? What is the function of the ribosomes? What is the function of the Golgi apparatus (body)? What is the function of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER)? What is the difference between the rough and smooth endoplasmic reticulum? • • • • • • • • • • • • • • Specialized subunits of cells that have a particular function Prokaryotes have a few (e.g., ribosomes) Eukaryotes have many, usually surrounded by a membrane This where we get the term “membrane-bound organelles” Also called plasma membrane Protects and supports the cell Controls what enters and leaves the cell It is a lipid bilayer (2 layers of fat cells) Found in all types of cells – prokaryotes and eukaryotes! Found in eukaryotic plant and protist cells; also in prokaryotes Main function is protection, rigidity, and support Outside of cell membrane Made of cellulose (a carb!) Allows water and dissolved substances to pass through Controls most activities in the cell Usually one per cell Contains DNA – the coded instructions for making proteins and other molecules for the cell The nuclear envelope has nuclear pores, where things can enter or leave Small, dense region in the middle of the nucleus This is where ribosomes are formed Clear fluid within cell that contains all organelles Moves materials throughout the cell Makes proteins in the cell May be free in cytoplasm or attached to ER Proteins are vital to life – all cells must produce them!!! Stacks of membranes used for storing, modifying, or packaging chemicals Packaged chemicals can be stored inside the cell or secreted outside the cell Cells that make saliva or mucus have many Golgi bodies Series of folded membranes that form sacs or tubes Two types – smooth and rough Rough ER: – Ribosomes make it look rough or bumpy – Ribosomes synthesize (make) proteins, so the Rough ER is where this happens! Smooth ER: – Smooth - no ribosomes! – Synthesizes (makes) lipids – Detoxifies drugs What is the function of lysosomes? What is the function of peroxisomes? What is the function of vacuoles? What is the function of chloroplasts? What is the function of the mitochondria? What is the function of the cytoskeleton? What is the function of centrioles? What is the function of the flagellum? What is the function of cilia and pili? Which organelles have their own set of DNA? • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • What is the evolutionary origin of mitochondria and chloroplasts? Summary: • Made by the Golgi Apparatus Full of digestive enzymes to digest unwanted particles Help white blood cells to destroy bacteria Clean-up crew! Filled with enzymes to digest toxic substances Numerous in the liver Do not form at Golgi Body Store food, water, or waste materials In plant cells, they are very large! Found in eukaryotic plant cells & some protist cells Capture light energy and convert it into chemical energy during photosynthesis Energy producers – the “powerhouse” of the cell! Convert chemical energy into useable energy Found in animal and plant cells Overlapping network of filaments and fibers that support the cell and help it maintain its shape Can also help cells move Microfilaments and microtubules Help to organize the cell during cell division They migrate to either side of the cell and help to pull it apart Only found in animal cells! Extension of the cytoskeleton- Allows movement, main source of transportation for cells Only some animals and some prokaryotes have these Extension of the cytoskeleton- Allows things to move around the cell. Propels mucus in your throat, helps with hearing in your ears, and helps move food particles in your stomach. Only some animal cells and some prokaryotes Only two organelles have their own DNA – mitochondria and chloroplasts. Among multicellular animals, nearly all of the mtDNA in a fertilized egg is inherited from only the mother. – One mechanism for this is simple dilution: an egg contains 100,000 to 1,000,000 mitochondria, whereas a sperm contains only 10 to 100. Endosymbiotic Theory: – Mitochondria and chloroplasts descended from ancient prokaryotes that developed symbiotic relationships with ancient cells. – In other words… mitochondria and chloroplasts are former prokaryotes that now “live” inside eukaryotes!