* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Test Study Guide
Survey
Document related concepts
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
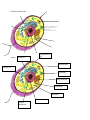
Cell Test Study Guide 1) How are cells organized? 2) What are the three parts to the cell theory? 3) What do chloroplasts and mitochondria have in common? 4) What limits how large a cell can grow? 5) What is the difference between a eukaryote and a prokaryote? 6) What does it mean when I say that the cell membrane is semipermeable/selectively permeable? 7) What two things is the cell membrane made out of? 8) The heart would be considered a what? Organ? Tissue? Cell? 9) How big are most cells? 10) What does the human excretory system do? Nervous system? 11) What do these organelles/structures do? Nucleus, mitochondria, ribosomes, endoplasmic reticulum, golgi apparatus, lysosomes, centrioles, cell wall, vacuole, chloroplasts, cell membrane, nuclear membrane 12) Be able to describe and understand how a microscope works and magnifies organisms. 13) Do both eukaryotes and prokaryotes have ribosomes? 14) When viewing an organisms under a microscope what happens as you go to a higher magnification? 15) Prokaryotes tend to be simple than eukaryotes. Why? Can they function as individual organisms? 16) Where are the traits of organisms stored? 17) How do the ER and Golgi apparatus work together? 18) What structures do both prokaryotes and eukaryotes have? Which ones do only eukaryotes have? Be able to label a cell. Cell Membrane Answer: Rough ER Mitochondria Smooth ER Lysosomes Golgi apparatus Ribosomes Cytoplasm Nucleus Nuclear Membrane